Figure 2.
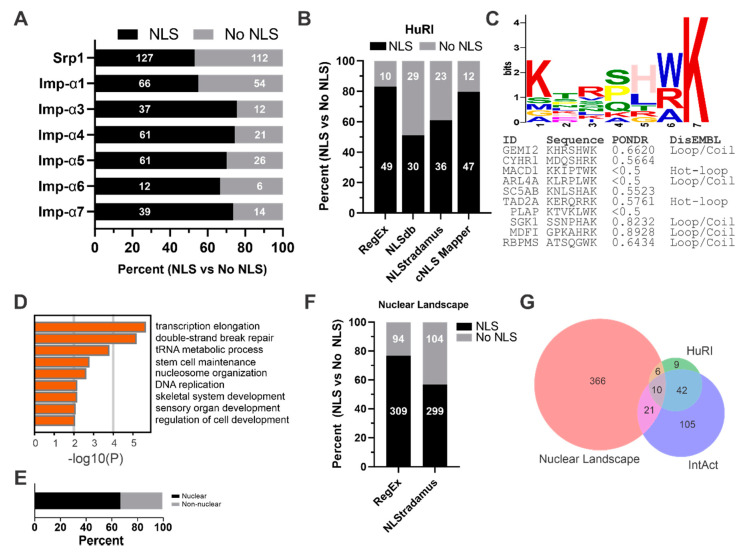
Many Imp-α cargo do not have a predictable cNLS. (A) Physical protein interactions, either direct or indirect, for yeast Srp1 and the indicated human Imp-α isoforms were retrieved from BioGrid and IntAct, and analyzed for cNLSs using RegEx matching. Prediction shows between 50% and 80% do not have a predictable cNLS. (B) Direct protein interactions for all Imp-α isoforms except Imp-α8 were retrieved from the Human Reference Interactome (HuRI). Interactors were pooled to remove redundant proteins, and checked against the HPA for evidence of nuclear localization before cNLS prediction. Several prediction programs were used to determine a range of predicted cNLSs, which demonstrated between 50% and 80% do not have a cNLS. (C) Proteins without a predicted cNLS from any of the prediction programs were processed with MEME to identify novel motifs common amongst each protein that might interact with Imp-α. Several of the motifs identified were rich in basic amino acids, but did not resemble a cNLS. Disorder prediction using PONDR (VSL2) and DisEMBL shows that these motifs are also found within disordered protein regions. (D) The motif KxRxHxK was searched against the human proteome using SLiMSearch, identifying 37 proteins, which were then analyzed with Metascape. Proteins bearing this motif are most enriched in core nuclear processes like RNA pol II transcription and DNA repair. (E) Proteins with the KxRxHxK motif were also checked against the HPA for evidence of subcellular localization. Of the 30 proteins with localization information, two-thirds have evidence of nuclear localization. (F) Reanalysis of the tandem mass spectra for protein interactions corresponding to Imp-α1, α5 and α6 from the Nuclear Landscape dataset. All significant interactions were checked against the HPA for nuclear localization before cNLS prediction. Between 50% and 75% of Imp-α cargoes do not have predictable cNLS when analyzed with NLStradamus and RegEx matching, respectively. (G) Identified proteins from the Nuclear Landscape dataset were compared to those from HuRI and IntAct. Comparison shows that the majority of protein identifications from the Nuclear Landscape dataset are not represented within these databases, and that these interactions show similar results in the number of proteins without predictable cNLSs.