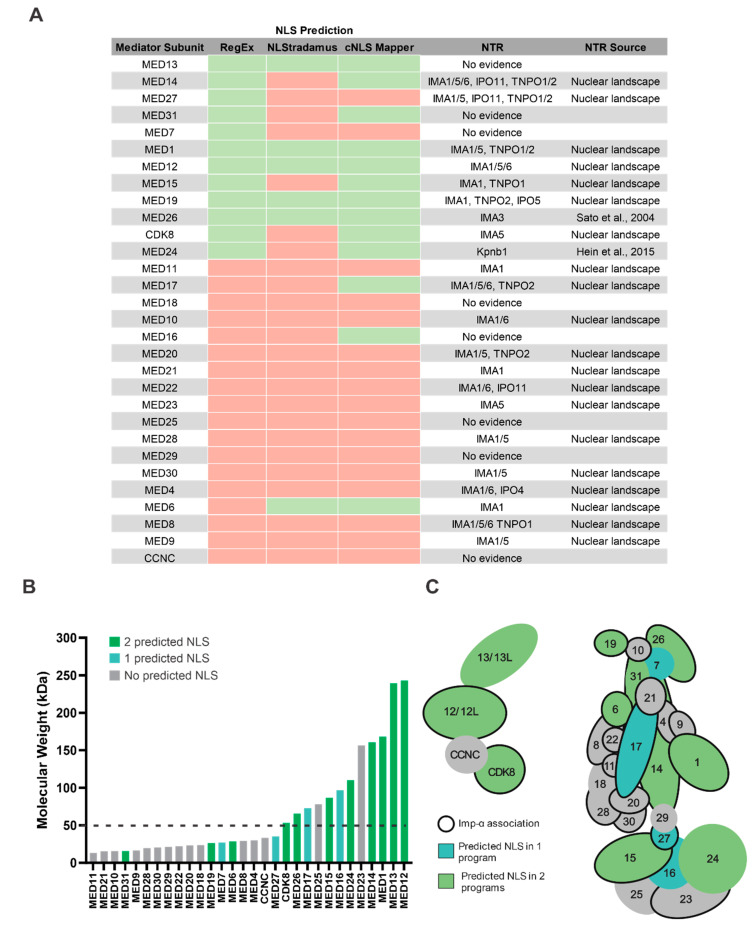
Figure 4.
Mediator complex subunits may utilize a piggybacking mechanism for nuclear import. (A) Mediator subunits were analyzed for cNLSs using different cNLS prediction programs, and data was tabularized using Microsoft Excel. Many subunits have a predicted cNLS (green) from more than one program, while the majority do not have a predicted cNLS (red). Data from the Nuclear Landscape dataset and other published nuclear transport receptor (NTR) interactions show that many subunits associate with Imp-α, as well as transportin (TNPO). (B) Mediator subunits vary in molecular weight, with larger subunits more frequently having a predicted cNLS. Subunits with a cNLS predicted from two programs or more are shaded in dark green (2 NLS) and those with a prediction from only one program are shaded in light blue (1 NLS). Although imprecise, a passive diffusion limit of 50kDa (dotted line) shows that many subunits without a cNLS are below this cut-off. (C) A model figure of Mediator was adapted from Soutourina, 2018, to show corresponding subunits with predicted cNLSs as well as Imp-α associations.