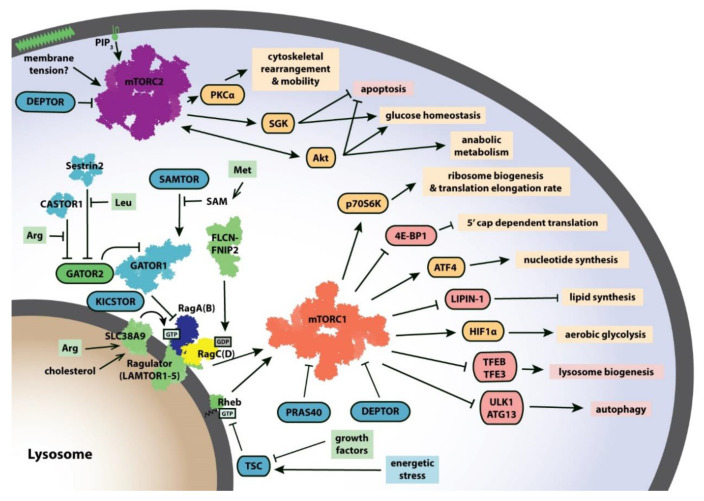
Figure 1.
mTORC1 and mTORC2 integrate cellular signals to promote cell growth. Cellular signals including growth factors, amino acid availability, and energetic status are communicated through a complex regulatory network that impinges on mTORC1 and mTORC2 to produce a variety of pro-growth outputs. Targets of mTORC1 and mTORC2 that are positively (shown in goldenrod) or negatively (shown in pink) regulated are listed with their downstream effects. Several known upstream regulators of mTORC1 and mTORC2 are shown (positive regulators in green, negative regulators in turquoise). Structures of mTORC1 (shown in orange, PDB: 6BCX), mTORC2 (shown in purple, PDB: 5ZCS), RagA/RagC (shown in navy/yellow) with Ragulator (PDB: 6U62), Rheb (PDB: 6BCU), FLCN-FNIP2 (PDB: 6ULG), and GATOR1 (PDB: 6CES), Sestrin2 (PDB: 5DJ4) and CASTOR1 (PDB: 5GT8) have provided new insights into how these proteins function and interact with one another. Abbreviations: 4E-BP1, 4E-binding protein 1; Arg, arginine; CASTOR, cellular arginine sensor for mTORC1; DEPTOR, DEP-domain-containing mTOR-interacting protein; FLCN, folliculin; GATOR, GAP activity towards the Rags; HIF1α, hypoxia inducible factor 1α; Leu, leucine; Met, methionine; P70S6K, p70 S6 kinase 1; PIP3, phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate; PKCα, protein kinase Cα; PRAS40, proline-rich AKT substrate 40 kDa; SAM, S-adenosylmethionine; SAMTOR, S-adenosylmethionine sensor; TFE3, transcription factor E3; TFEB, transcription factor EB; TSC, tuberous sclerosis complex; ULK1, unc-51-like autophagy-activating kinase 1.