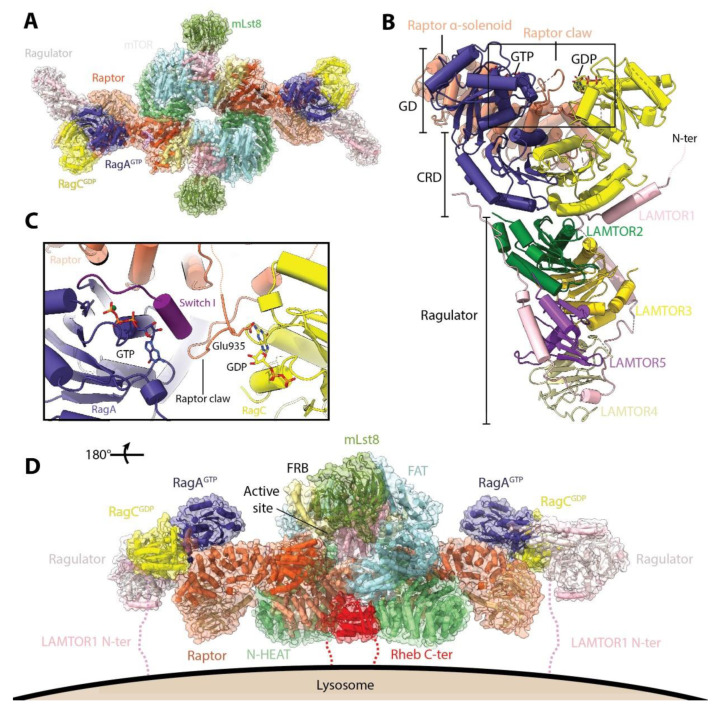
Figure 3.
Structure of mTORC1 regulators Rag-Ragulator and Rheb. (A) Model of mTORC1 bound to RagA/RagC and Ragulator (based on PDB: 6BCX, 6SB0, and 6U62). The RagA/RagC heterodimer interacts with mTORC1 via Raptor. (B) Structure of Raptor-RagA/RagC-Ragulator super complex (PDB: 6U62). The domains of RagA/RagC are indicated: GD, G-domains; CRD, C-terminal roadblock domains. Only the raptor α-solenoid is shown for clarity. Ragulator binds to RagA/RagC via their CRD, while Raptor binds to the GD on the opposite end of the heterodimer. (C) Close-up of the interaction between Raptor claw and RagA/RagC. Raptor residue Glu935 comes into close proximity to the RagC-bound nucleotide. (D) Model of activated mTORC1 anchored to the lysosomal membrane. Model was constructed as in (A) but using the mTORC1-Rheb structure (PDB: 6BCU). The complex is anchored via both the N-terminal tail of LAMTOR1 and the C-terminus of Rheb, both of which undergo lipid modifications.