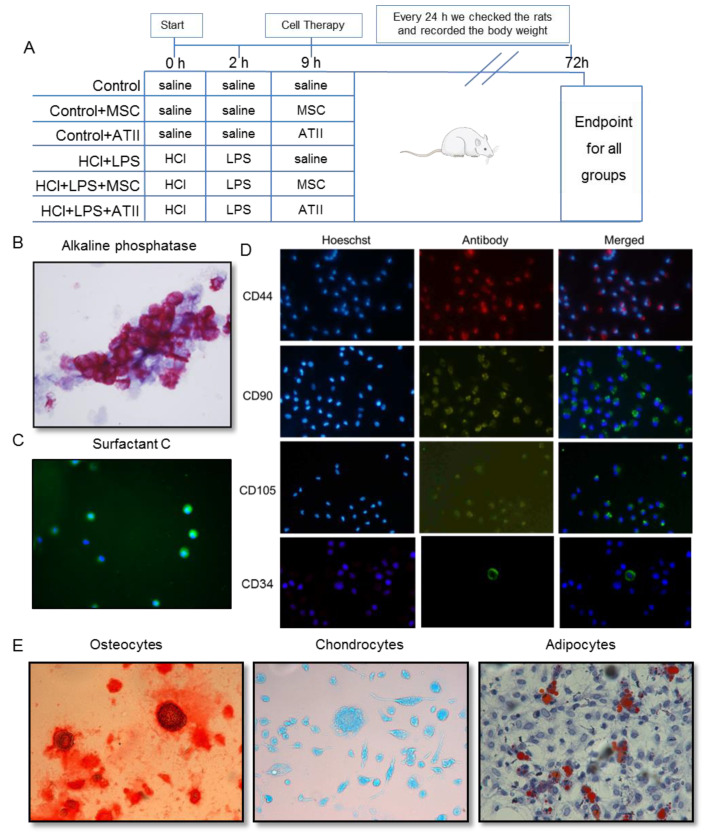
Figure 1.
Experimental procedure schema and multipotent mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) and alveolar type II cell (ATII) purity. (A) Animal experimental design: rats of 200–225 g body weight at the beginning of the experiment were randomized in six experimental groups as indicated. At 0, 2, and 9 h an intratracheal instillation was administered as indicated; the body weights were recorded every 24 h; and all the animals were sacrificed 72 h after starting the experiment. (B) Alveolar type II (ATII) cells stained with alkaline phosphatase (100×). In dark pink, we can identify the positive cells, therefore the real ATII. The purity for the ATII cells was 86 ± 3%. (C) Surfactant C staining for alveolar type II cells. Surfactant C (in green, fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)) and nuclear staining (in blue, Hoechst 33342) to confirm the ATII cell purity. (D) Mesenchymal stem cells stained by CD44 (in red, Texas Red), CD90 (in green, FITC), CD105 (in green, FITC), and CD34 (in green, FITC). Nuclei can be observed in blue by Hoechst 33342 staining. Magnification used is 100×. MSC should express CD44, CD90, and CD105 and should be negative for CD34. (E) MSC were differentiated into different lineages. Panel E shows the differentiation to osteocytes stained with Alizarin Red, to chondrocytes stained with Alzian Blue, and to adipocytes stained in oil-red -O staining (200× magnification). The purity of MSC was 78 ± 5%.