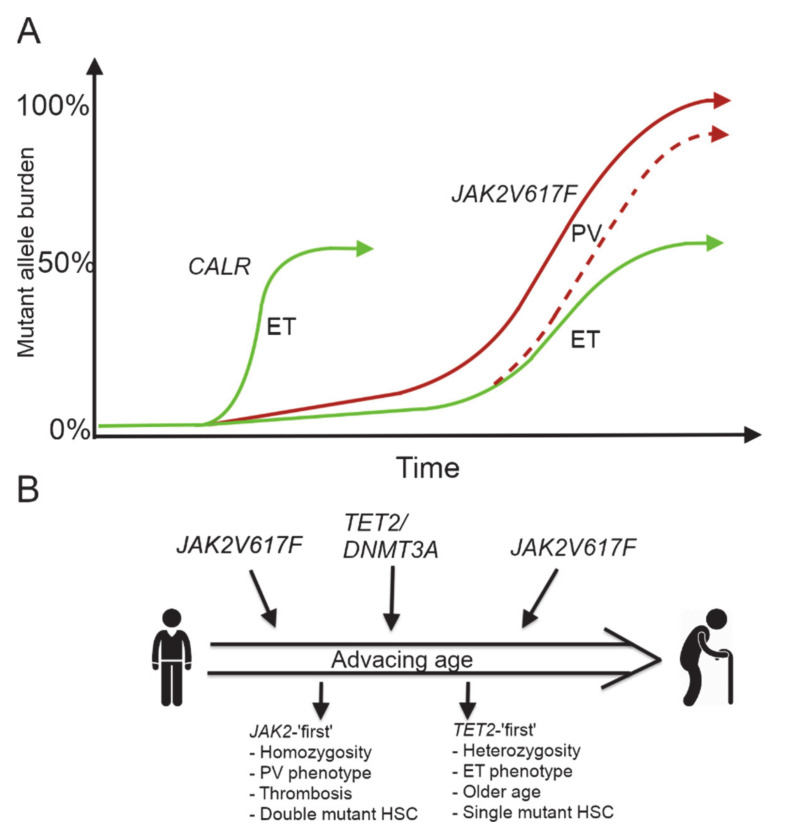
Figure 2.
Expansion of the MPN clone is affected by both the type of phenotypic driver and co-mutation acquisition order. (A) The CALR allele burden is considered to expand rapidly but homozygosity is rare and is virtually always associated with the essential thrombocythemia (ET) phenotype (green curve to the left). Different disease trajectories are seen for patients carrying the JAK2V617F mutation. Homozygosity for the mutation arises frequently in patients, but a homozygous clone is more likely to become the dominant in patients diagnosed with polycythemia vera (PV) (red curve). The ET trajectory for patients carrying the JAK2V617F (green curve to the right) will occasionally progress into a PV phenotype indicating a ‘biological continuum’ from ET to PV (dashed red line). (B) The acquisition order of JAK2V617F relative to TET2 and DNMT3A influences the disease phenotype. If the JAK2V617F occur prior to TET2 this results in a more severe phenotype, with the homozygous JAK2V617F/TET2 clone becoming dominant, whereas TET2 first leads to a predominantly heterozygous phenotype, where the JAK2V617F clone is reluctant to outcompete the TET2 mutated clone.