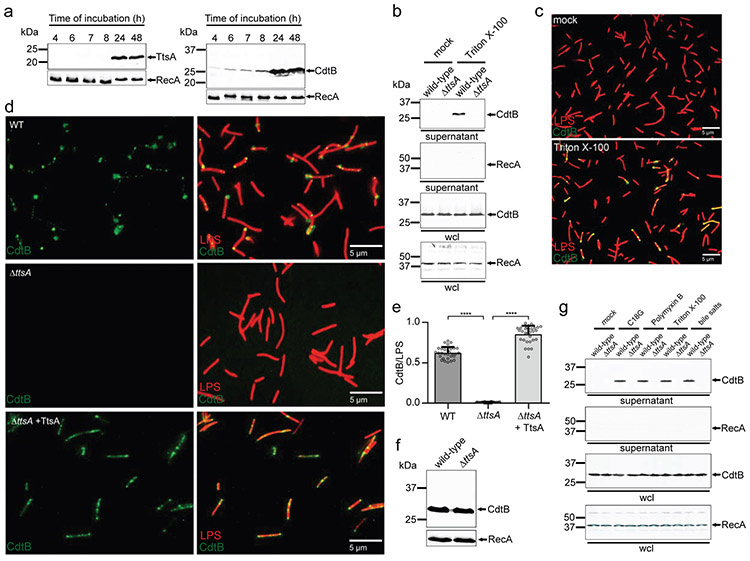
Figure 1. TtsA-dependent translocation and agonist-mediated release of typhoid toxin in vitro.
(a) Expression of TtsA and typhoid toxin in typhoid toxin inducing media (TTIM). S. Typhi carrying chromosomally encoded FLAG-tagged CdtB (as a surrogate for typhoid toxin) or TtsA were grown in TTIM and the expression of TtsA and CdtBin equal number of bacterial cells was monitored over time by Western blot analysis. The amount of RecA (loading control) was analyzed on a separate Western blot, (b-e) Outer membrane disruption results in the TtsA-dependent detection of typhoid toxin in culture supernatants and on bacterial cells. Wild-type and ΔttsA S. Typhi (CdtB-FLAG) were grown in TTIM for 24 hs, pelleted and washed twice with PBS, and subsequently treated with Triton X-100 (0.1 %). Bacterial whole cell lysates (wcl) and filtered culture supernatants were then analyzed by Western blotting for the presence of CdtB and RecA (as a cell lysis and loading control) (b). Alternatively, wild-type S. Typhi was grown 24 hs in TTIM, fixed, treated with Triton X-100 (0.1%) or PBS (mock), and then stained with mouse anti-FLAG (to stain CdtB) (green) and rabbit anti S. Typhi LPS (to visualize bacterial cells) (red) (c). (d and e) The indicated strains grown in the same manner were fixed, treated with Triton X-100 (0.1 %) and stained as indicated above. The average ratios of typhoid toxin positive cells (green) vs total cells (LPS, red) ± standard deviation are shown (**** p < 0.0001, two-sided Student’s t Test) (Supplementary data set 1) (e). The levels of CdtB in the strains used in panel (c) were determined by Western blot analysis using RecA as a loading control analyzed on a separate Western blot (f). (g) Antimicrobial peptides trigger the release of typhoid toxin to the culture supernatants. Wild-type and ΔttsA S. Typhi strains (CdtB-FLAG) CdtB were grown 24 hs in TTIM, pelleted and washed twice with PBS and subsequently treated with sub-inhibitory concentrations of the antimicrobial peptide C18G (2.5μg/ml) for 30 min, Polymyxin B (0.1μg/ml), Triton X-100 (0.1%), or bile salts (0.05 %). Filtered supernatants and whole cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting for the presence of CdtB and RecA (as a cell lysis and loading control). All data in (a-g) were derived from at least three independent experiments.