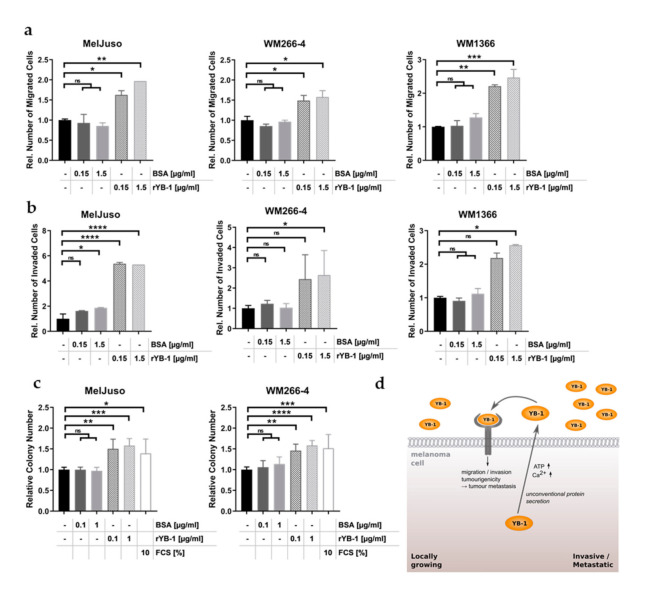
Figure 6.
Extracellular YB-1 stimulates migration, invasion, and in vitro tumourigenicity of melanoma cells. (a,b) Boyden chamber-based cell migration (a) or invasion assay (b) after stimulation with rYB-1 (0.1 µg/mL, 1 µg/mL) or BSA (0.1 µg/mL, 1 µg/mL). The relative number of migrated (a) and invaded (b) cells was calculated based on the evaluation of five optical fields and normalised to the respective untreated controls (mean ± SD, n = 2). Significance was determined by one-way ANOVA with subsequent Tukey’s multiple comparisons test (ns = non-significant, * for p < 0.05, ** for p < 0.01, *** for p < 0.001 and **** for p < 0.0001). (c) Anchorage-independent growth assays of melanoma cells stimulated with rYB-1 (0.1 µg/mL, 1 µg/mL), BSA (0.1 µg/mL, 1 µg/mL), or 10% FCS. Colony numbers were normalised to the respective untreated controls (mean ± SD, N = 2 with n = 2). One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test was used to assess significant differences (ns = non-significant, * for p < 0.05, ** for p < 0.01, *** for p < 0.001 and **** for p < 0.0001). (d) Schematic graph depicting the functional effects of extracellular YB-1 as well as its secretion from melanoma cells.