Figure 2. CD31 expression in ASM angiosarcoma cells separates vasoformative ‘organotypic’ CD31high cells from the more aggressive CD31low cells with spindle cell morphology.
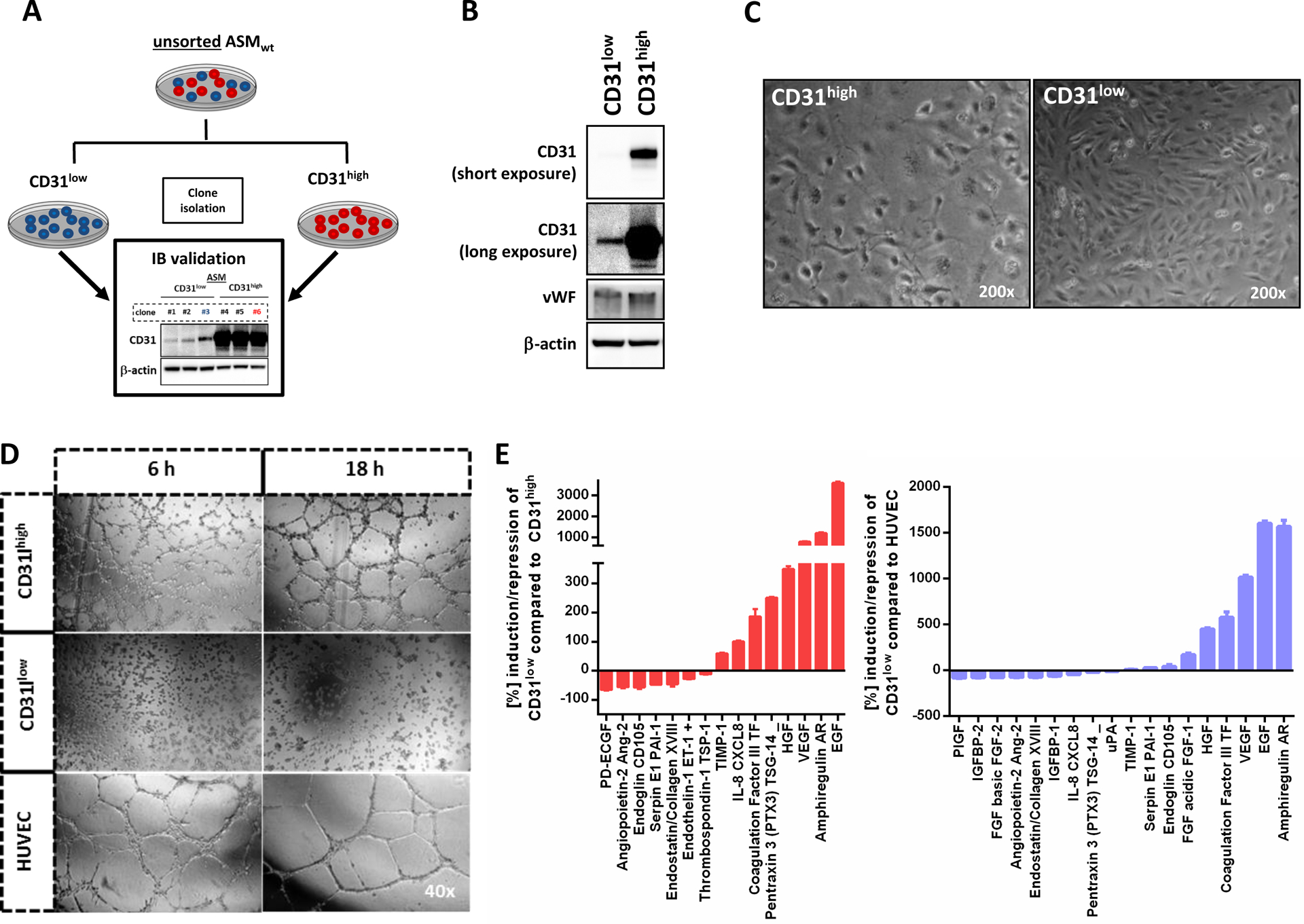
(A) Schematic summary of the experimental protocol used to isolate CD31high and CD31low fractions from the ASM cell line. Unsorted ASMwt (wild-type) cells were stably transduced with the empty pLK0.1 vector under puromycin selection. Subsequently, surviving single clones with picked and immunoblotted (IB validation) for CD31 and classified as CD31high or low CD31low cells. Repetitive CD31-FACS analysis from CD31high (clone #3) and CD31low (clone #6) and Western blot demonstrated stable levels of CD31 up to 44 passages (data not shown). (B) Western blot analysis revealed only differential expression of CD31, but not of von-Willebrand factor (vWF), suggesting that both populations were endothelial cells. Longer exposure was needed to detect the presence of CD31 in CD31low cells. (C) Microscopic images of CD31high and CD31low cells showing a polygonal cell shape in non-confluent CD31high cells and cobblestone pattern upon confluence. In contrast, CD31low cells had a more fibroblastic, spindle cell morphology. (D) HUVEC formed organized networks of tubular endothelial structures which matured after 6 hours and even presented signs of degradation after 18 hours. In CD31high cells, pre-tubular structures could be detected after 6 hours and mature tubes after 18 hours. In strong contrast, CD31low cells did not show tubular structures at any time point, even after extended observation for up to 24 hours (data not shown). (E) In a screening of 55 angiogenesis-associated proteins, 18 factors with both pro- and antiogenic properties were differentially expressed in CD31low compared to CD31high cells and HUVEC (n=2).
