Figure 6. Validation of CD31 as a YAP-dependent regulator of redox functions in angiosarcoma cells.
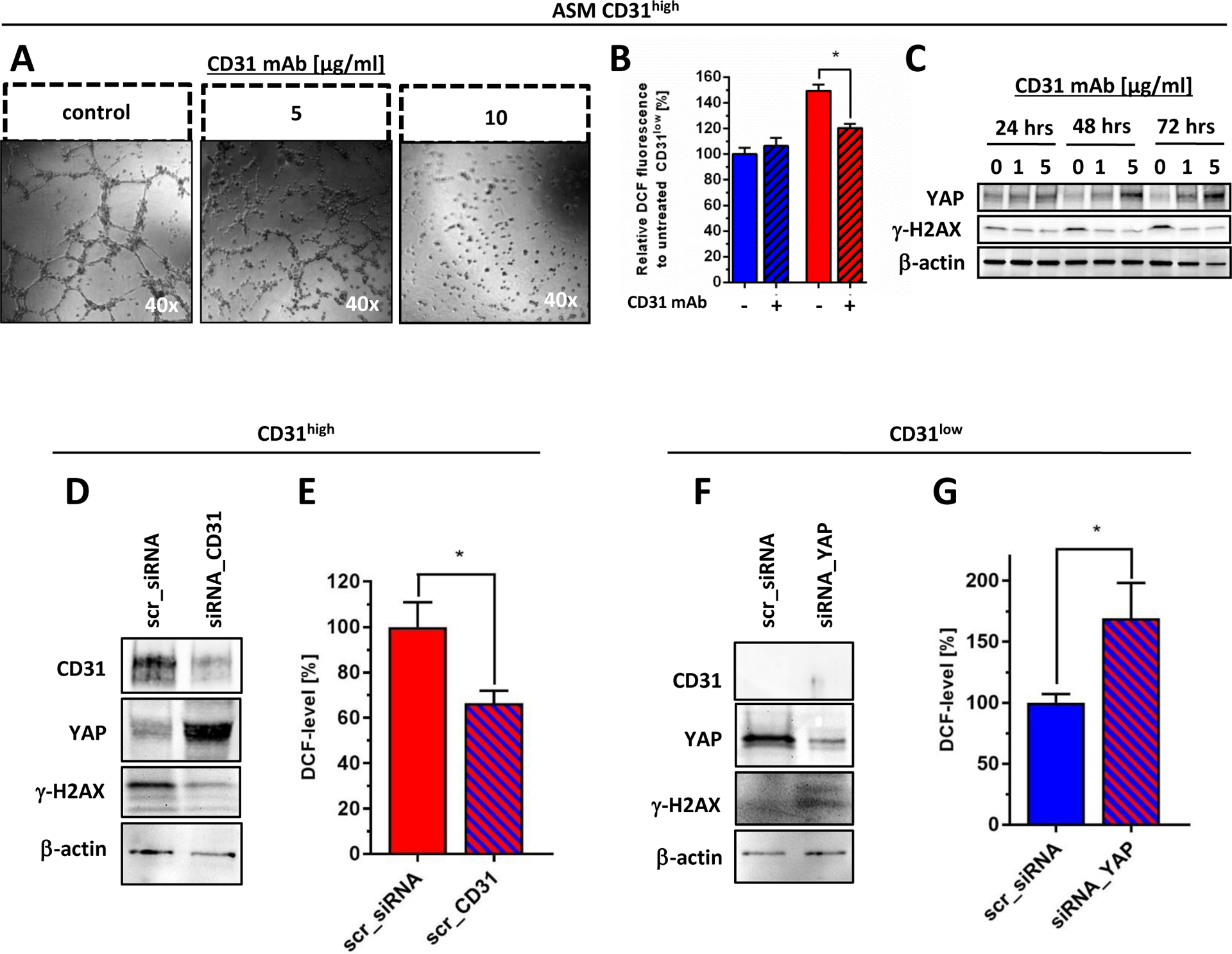
(A) CD31high cells lost their tube forming capacity after treatment with an anti-CD31 blocking monoclonal antibody (CD31 mAb) for 18 hours in a concentration-dependent fashion. (B) Treatment with CD31 mAb for 24 hours effectively reduced basal oxidative stress levels (indicated by flow cytometric DCF staining) selectively in CD31high cells, while similar treatment did not alter ROS level in CD31low cells. (C) Immunoblot anaylsis demonstrated that CD31 mAb treatment in CD31high cells under 1% serum-starvation induced YAP expression that was paralleled by decreased levels of γ-H2AX, indicating attenuated basal oxidative DNA damage. Medium with or without CD31 mAb was replaced every 24 hours. (D) CD31high cells were treated either with selective siRNA against CD31 (siRNA_CD31) or scrambled sequence (scr_siRNA). Immunoblot analysis was performed 48 hours after transfection showing selective knockdown of CD31, together with a marked increase of YAP and suppression of oxidative DNA, indicated by γ-H2AX. (E) Flow cytometric quantification of DCF fluorescence at the same time point showed a significant increase of endogenous oxidative stress levels in YAP-depleted CD31low cells compared to scrambled transfected controls (n=3). (F) Selective knockdown of YAP (siRNA_YAP) in CD31low cells resulted in a marked induction of γ-H2AX compared to scrambled transfected controls (scr_siRNA), 48 hours after transfection. (G) Flow cytometric quantification of DCF fluorescence at the same time point showed a significant increase of endogenous oxidative stress levels in YAP-depleted CD31low cells compared to scrambled transfected controls (n=3). All data are mean ± SEM and were analyzed using either two-way ANOVA (B) or unpaired t-test (E, G) (*p < 0.05).
