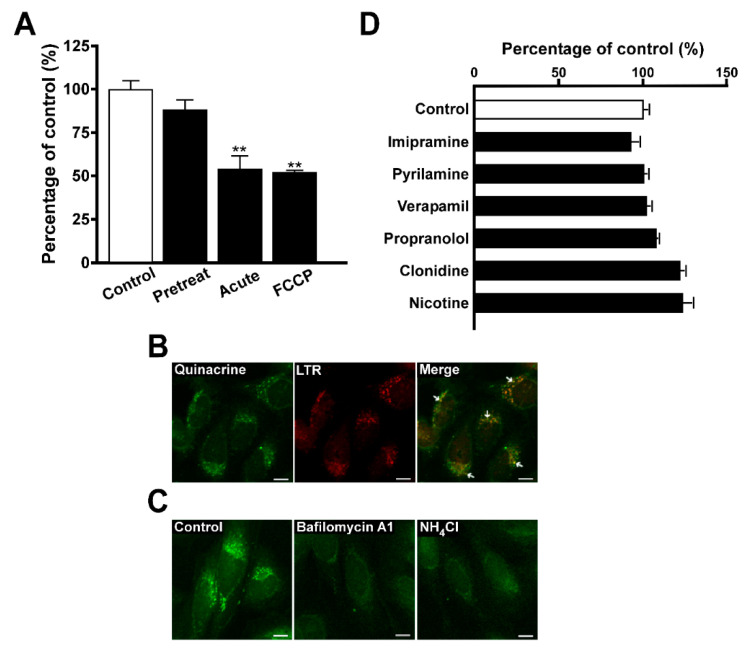
Figure 2.
Effect of intracellular pH modulators on quinacrine uptake by TR-iBRB2 cells. (A) The quinacrine uptake was examined in the presence or absence of 30 mM NH4Cl at 37 °C for 30 min. In a pretreat condition, cells were treated with 30 mM NH4Cl, and the uptake of quinacrine (5 μM) was performed in the absence of NH4Cl. In an acute condition, cells were treated with ECF-buffer, and quinacrine uptake was performed in the presence of 30 mM NH4Cl. The uptake was also examined in the presence of 50 μM FCCP at 37 °C for 30 min. (B) Confocal microscopy was carried out to investigate the intracellular distribution of quinacrine and LTR. The uptake of quinacrine (5 μM, green) and LTR (300 nM, red) was carried out at 37 °C for 30 min. (C) Confocal microscopy was carried out to investigate the intracellular distribution of quinacrine in the presence of intracellular pH modulator, such as 100 nM bafilomycin A1 and 30 mM NH4Cl. The uptake of quinacrine (5 μM, green) was carried out at 37 °C for 30 min. (D) Inhibitory effect of cationic drugs on quinacrine uptake was examined in the presence of bafilomycin A1. After the treatment of TR-iBRB2 cells with 100 nM bafilomycin A1 at 37 °C for 30 min, quinacrine uptake was examined in the presence of 100 μM cationic drug at 37 °C for 30 min. Each column represents the mean ± S.E.M. (n = 3–4). ** p < 0.01, significantly different from the control. FCCP, Carbonyl cyanide-p-trifluoromethoxyphenylhydrazone. Scale bar, 10 μm.