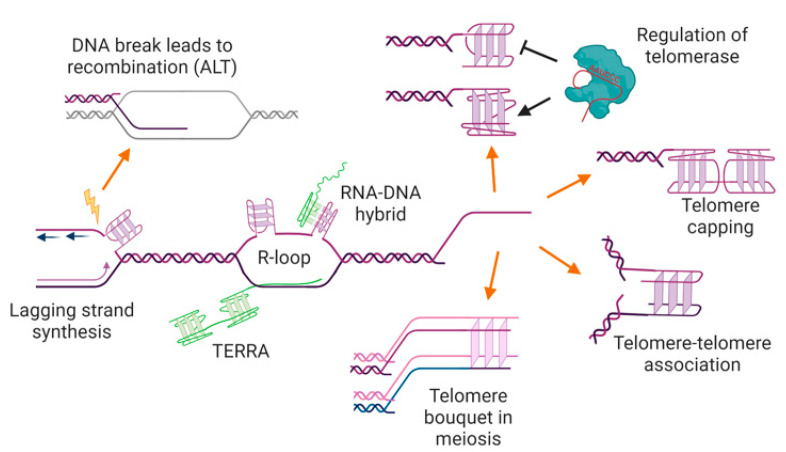
Figure 4.
Potential locations, functions, and consequences of G-quadruplexes at telomeres. G-quadruplexes may form in the single-stranded telomere overhang, where they may positively or negatively regulate telomerase and/or have a capping function, preventing access to the DNA repair machinery. G-quadruplexes at overhangs may also mediate interactions between two telomeres (e.g., during sister chromatid cohesion, or in the macronucleus of ciliated protozoa), or be involved in telomere clustering in meiosis. G-quadruplexes could also form in the double-stranded region of the telomere during DNA replication or transcription, where they may trigger genome instability and/or recombination-mediated telomere maintenance. The RNA transcribed from telomeres, TERRA, can also form into G-quadruplexes, either unimolecular or as an RNA-DNA hybrid. See text for details and references. Figure created with BioRender.com.