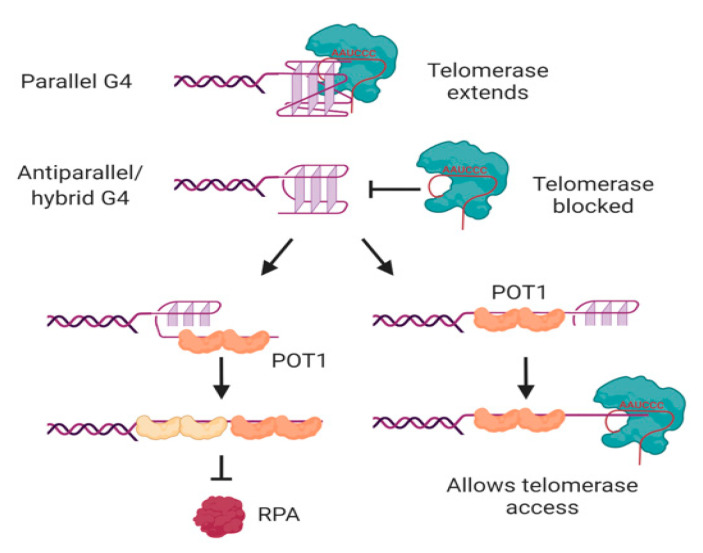
Figure 5.
Interactions of telomerase, POT1 and RPA with human telomeric G-quadruplexes. Telomerase can bind and extend parallel, but not antiparallel or hybrid, G-quadruplexes. POT1 binds to antiparallel or hybrid G-quadruplexes through a mechanism in which G4 unfolding precedes “trapping” of the unfolded DNA by POT1. The two OB folds of each POT1 molecule bind to consensus binding site TTAGGGTTAG; sequential binding of two POT1 molecules therefore coats the 4-repeat telomeric DNA (left). Although RPA also has the ability to unwind G-quadruplexes, POT1 competes with this activity. If binding of POT1 occurs at the 5′ region of the DNA, the 3′ tail can form a substrate for telomerase (right). Not shown is POT1’s binding partner TPP1, which also influences G4 unwinding dynamics and telomerase activity. See text for details and references. Figure created with BioRender.com.