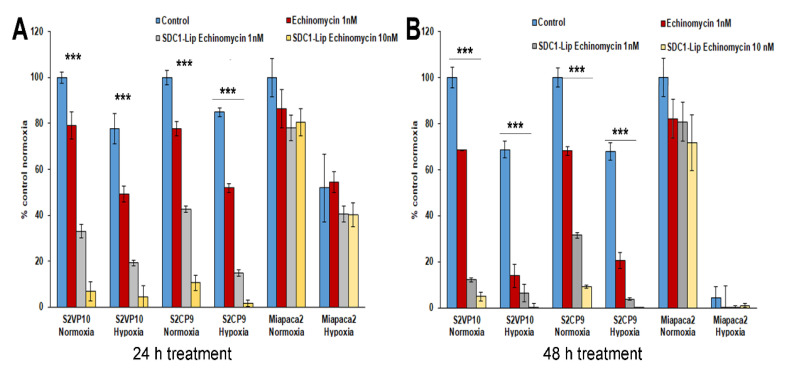
Figure 2.
Treatment of pancreatic cancer cells with SDC1-Lip echinomycin under normoxic and hypoxic conditions. S2VP10, S2CP9, and Miapaca2 cells were treated with echinomycin-alone (1nM), SDC1-Lip echinomycin (1 nM or 10 nM) under normoxic and hypoxic conditions for (A) 24 or (B) 48 h. (A) SDC1-Lip echinomycin treatment (1nM and 10nM) reduced the viability of both S2VP10 (33.0% or 6.7%) and S2CP9 (42.6% or 10.6%) cells cultured under normoxic conditions (p = 0.00001, p < 0.00001, p = 0.00001 and p < 0.00001, respectively) compared to untreated controls. Similar treatment also reduced the viability of both S2VP10 (p = 0.001, p < 0.00001) and S2CP9 (p = 0.001, p < 0.00001) cells compared to the free echinomycin (1 nM and 10 nM) controls. (B) After 48 h, treatment of SDC1-Lip echinomycin (1 nM) significantly reduced viability of both S2VP10 (12.1%) and S2CP9 (31.5%) cells (p < 0.00001 and p = 0.00001) compared to PBS-treated controls. Treatment with SDC1-Lip echinomycin 10 nM further enhanced the cytotoxicity in a dose-dependent manner in S2VP10 (4.8%) and S2CP9 (9.1%) (p < 0.00001). Following exposure of cells to hypoxic conditions, S2VP10 and S2CP9 cells treated with SDC1-Lip echinomycin treatment (1 nM and 10 nM) also showed a decrease in viability (p = 0.001, p < 0.001; p = 0.002, p < 0.003, respectively) when compared to free echinomycin (1 nM and 10 nM) controls. (p < 0.00001). *** p < 0.001