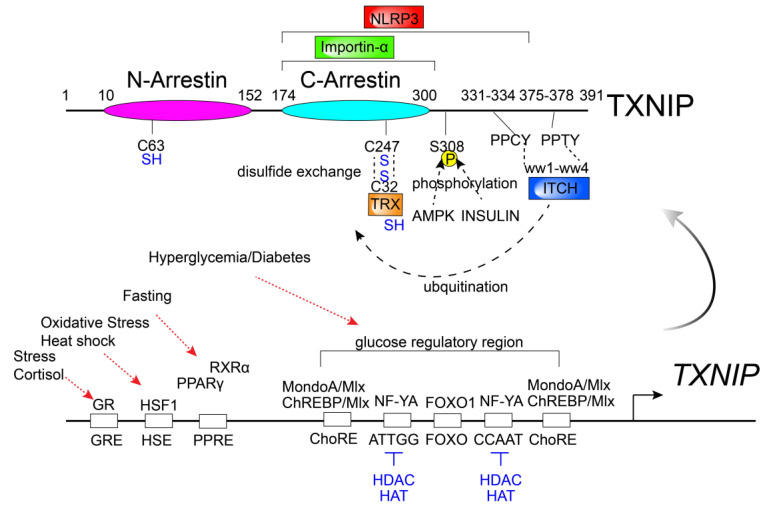
Figure 2.
Transcriptional and post-translational modification and protein interacting domains of TXNIP. TXNIP gene expression is regulated by various stimuli. Post-translational modifications and protein interactions of TXNIP influence its protein stability, localization and function in a cellular and context-dependent manner. Protein scaffolding and the biological function of TXNIP are biased in the C-arrestin domain. Two PPxY motifs (PPCY and PPTY) of Txnip bind to the four WW domains of E3 ubiquitin ligase, ITCH. Insulin and AMPK facilitate the protein degradation by serine 308 (S308) phosphorylation of TXNIP. TXNIP forms disulfide bonds with reduced TRX by disulfide exchange through its cysteine 247 (C247). Glucocorticoid–glucocorticoid responsive element (GR–GRE), heat shock factor 1–heat shock element (HSF1–HSE), peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ/retinoid X receptor α–peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor element (PPARγ/RXRα–PPRE), MLX interacting protein/Max-like protein X (MondoA/Mlx – ChoRE) or carbohydrate-responsive element-binding protein/Max-like protein X–carbohydrate response element (ChREBP/Mlx-ChoRE), nuclear transcription factor Y subunit α–CCAAT motif (NF-YA–ATTGG/CCAAT), Forkhead Box O1 (FOXO1)–putative FOXO1 binding site (FOXO).