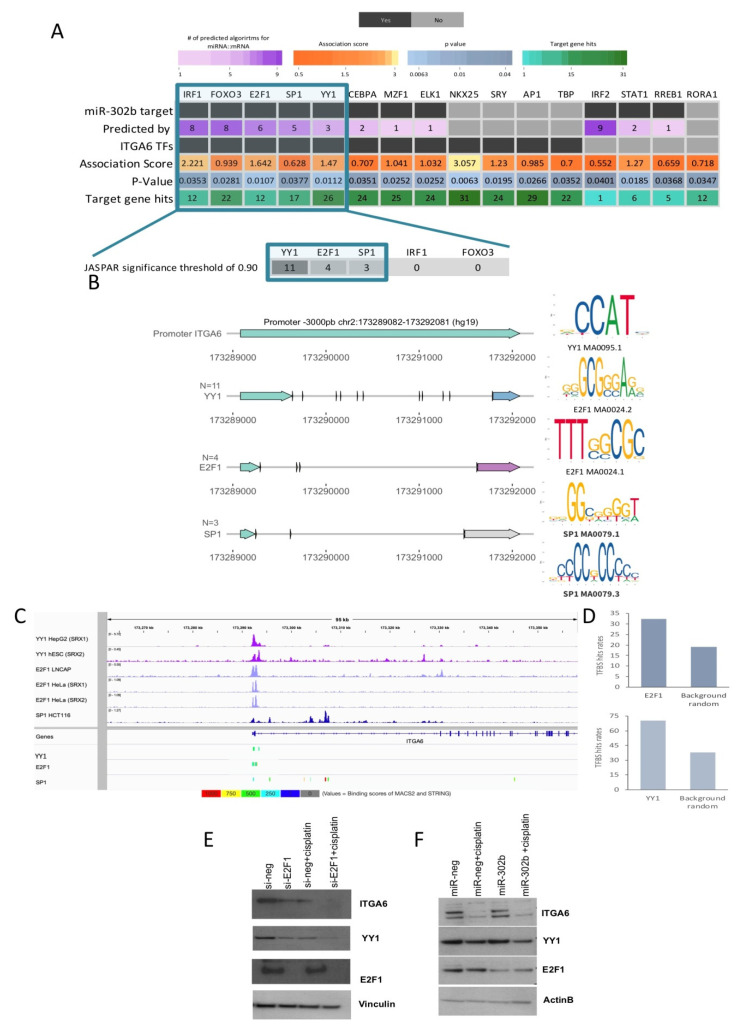
Figure 4.
Summary of ITGA6 putative transcription factors (TFs) and their role behind the established mechanism by the combinatorial effect of miR-302b and cisplatin. (A) Overview of the study strategy to define possible TFs regulating ITGA6 expression. Through weight TFs matrices enrichment methods of down-modulated genes in the in vivo assay (miR-302+cisplatin versus cel-miR-67 negative control+cisplatin) possible TFs were identified. Only those TFs predicted as miR-302b targets and presenting motif binding sites to the promoter sequence of ITGA6 were considered (highlighted in blue square). Bottom zoom panel shows the top TF candidates and the number of robust bindings sites to ITGA6 promoter computed by JASPAR (significance threshold > 0.9). The square highlights the selected TFs. (B) Schematic representation of the robust binding sites of YY1, E2F1, and SP1 on the ITGA6 promoter. Right panel shows the TFs motif from the JASPAR database used in the analysis. (C) Representative images of Chip-seq peaks of the selected TFs obtained by ChIP-Atlas and visualized in Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV). (D) Frequency of E2F1 and YY1 TFBS hits among downregulated genes compared to hits in a set of background random genes. ITGA6, YY1, and E2F1 expressions following si-E2F1 knockdown (E) and miR-302b transfection (F) in MDA-MB-231 cells treated or not with cisplatin. Vinculin and β-actin were used as housekeeping controls. Data are representative of three independent experiments performed at least in triplicate.