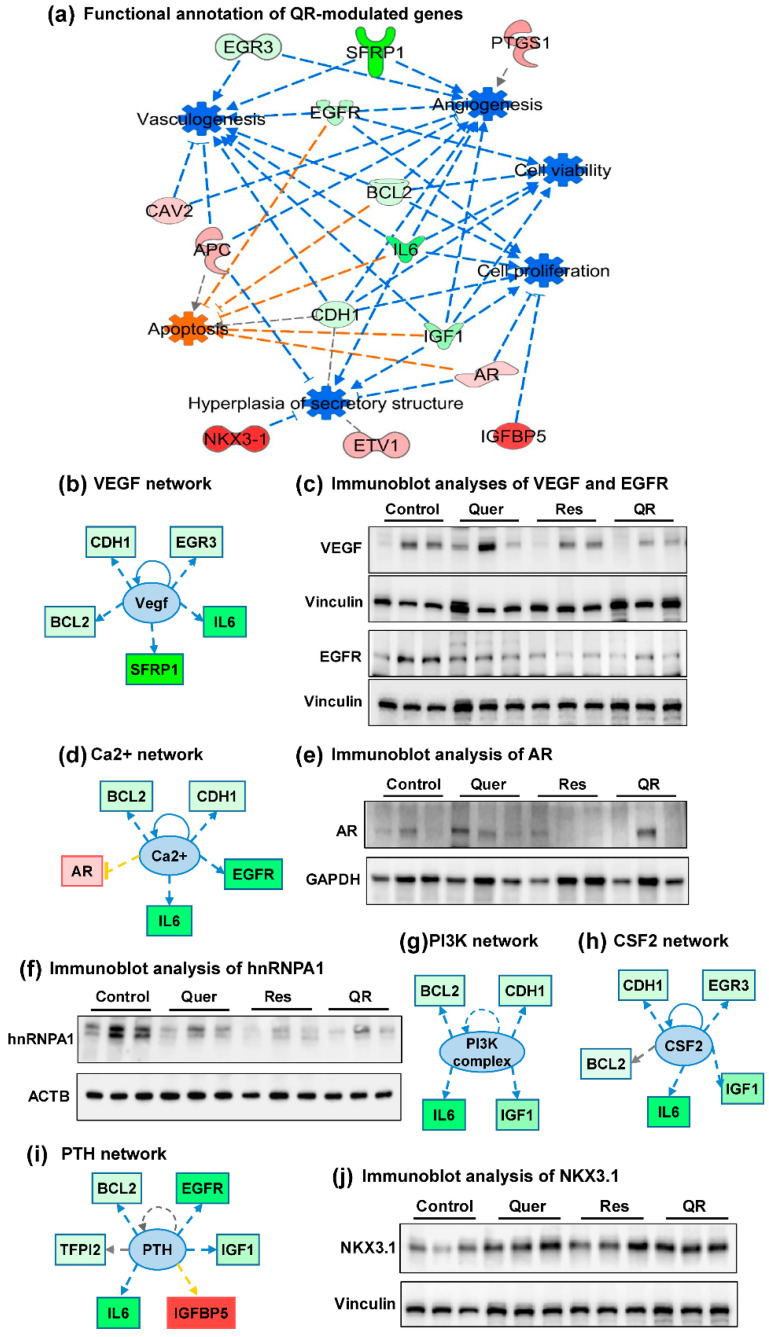
Figure 6.
Analysis of quercetin–resveratrol (QR)-modulated genes suggest cumulative antitumor actions and upstream inhibition of major PCa signaling pathways. (a) Functional annotation showing cumulative actions of QR-modulated genes: increased apoptosis and inhibition of cell viability/ proliferation, hyperplasia, vasculogenesis, and angiogenesis. (b,d,g–i) Using IPA, upstream regulator analysis identified genes potentially involved in changes seen in RT-qPCR analyses. Genes from array are in red (upregulated) and green (downregulated), while predicted functions and upstream regulator genes and interaction lines are in orange (activation) and blue (inhibition). Lines in yellow indicate findings inconsistent with the state of downstream molecules. The gray dotted line shows unpredicted effects. Immunoblot analyses of (c) vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), (e) androgen receptor (AR), (f) hnRNPA1, and (j) NKX3.1 proteins. Vinculin, ACTB, and GAPDH were used as loading controls.