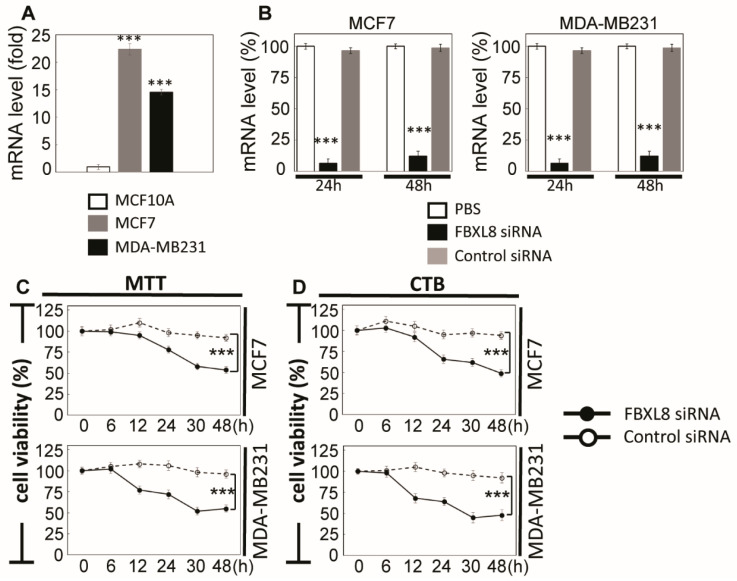
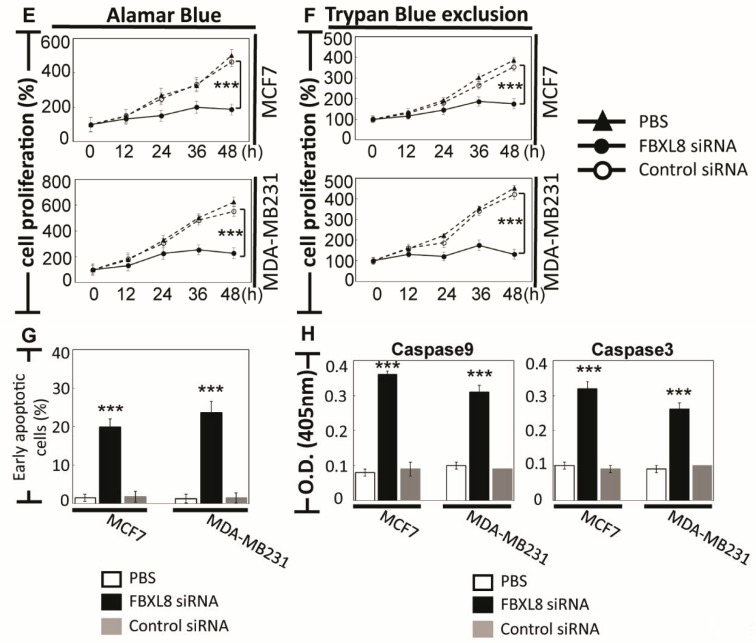
Figure 3.
FBXL8 plays a critical anti-apoptotic role in BRCA. To elucidate the functional role of FBXL8 in breast carcinoma, we analyzed various human breast cancer cell lines: MCF-7 and MDA-MB231, compared to a non-cancer control breast cell line, MCF10A. (A) qRT-PCR shows the endogenous levels of FBXL8 mRNA in MCF7 and MDA-MB231, compared to MCF10A cells. FBXL8 mRNA is significantly upregulated in breast carcinoma cells. (B) qRT-PCR analysis was used to measure the RNAi efficacy. Optimized transfection efficacy with FBXL8-specific siRNA is shown in both MCF7 and MBA-MD231 cells. Knockdown efficiency was optimal at 24 h where, up to 95% loss of FBXL8 mRNA was achieved in both cell lines, compared to controls using PBS (phosphate buffered saline) and scrambled siRNA (***, p < 0.001). The cell viability of FBXL8 knocked down BRCA cell lines was significantly reduced as shown by: (C) MTT and (D) CTB assays. For each time point, cell counts were normalized to the corresponding PBS-treated controls. (E) Alamar Blue or (F) Trypan Blue exclusion tests showed significant reduction in cell proliferation. (G) Annexin V and 7-aminoactinomycin (7-AAD) double staining was conducted to examine early apoptosis (AnnexinV+/7AAD−, red box). (H) FBXL8-siRNA knockdown of MCF7 and MDA-MB231 cells underwent apoptosis via activation of Caspases -9 and -3, suggesting that presence of FBXL8 is pivotal to anti-apoptosis in BRCA. Representative histograms of apoptosis assay are shown in Figure S5. Data are means ± SD (n = 3). ***, p < 0.001.