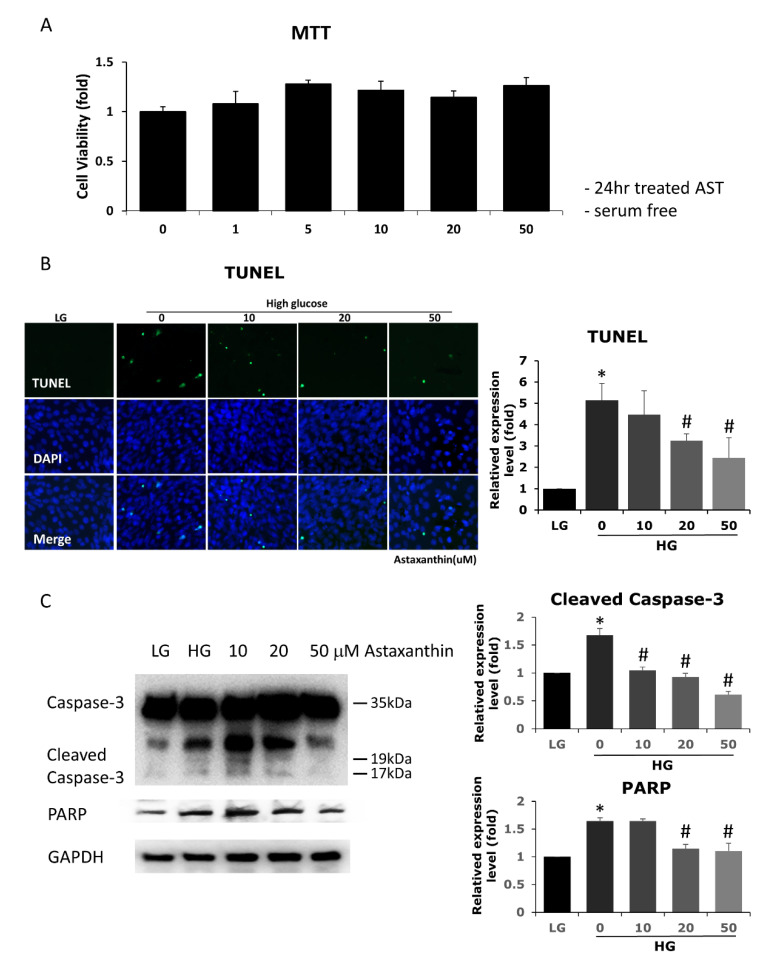
Figure 1.
Effects of AST on cell viability and high glucose-induced apoptosis in 661W cells. (A) Cell viability was evaluated using MTT assay upon treatment with different concentrations of AST for 24 h. AST-treated and control cells showed similar cell viability. (B) Increased cell apoptosis was noted under high glucose environment, demonstrated by TUNEL assay and protein expression (western blots, C). AST reduced apoptosis at 20 and 50 μM concentration. (C) Decreased cleaved caspase-3 and PARP protein expression seen in western blots indicated that apoptosis was attenuated by AST. AST = astaxanthin; HG = high glucose; LG = low glucose; MTT = 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide; TUNEL = terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling; PARP = poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase; GAPDH = glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. * Significantly different from control group (p < 0.05); # significantly different from high glucose-treated group without AST (p < 0.05). The Mann–Whitney U test was used to calculate the differences between the means of different experimental groups (three repeats per experiment, three wells per repeat, five images per well analyzed).