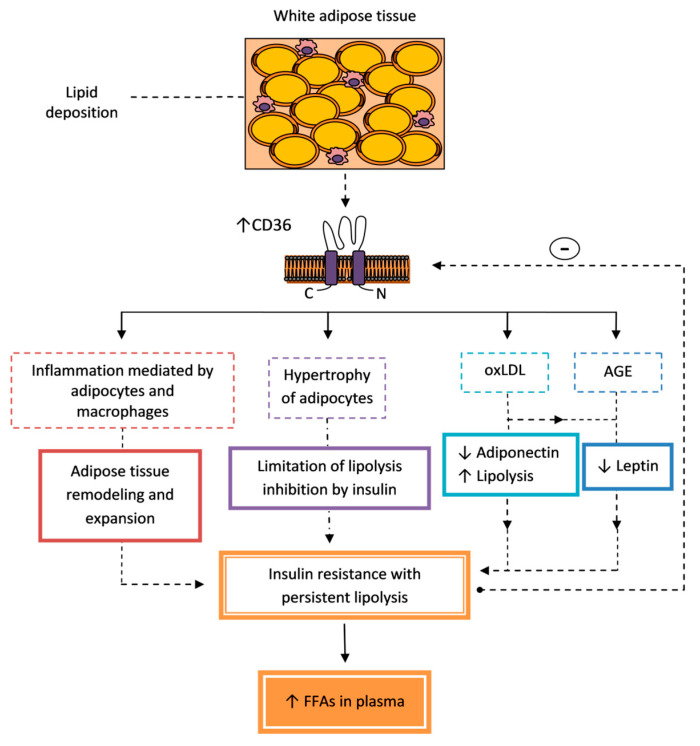
Figure 1.
The contribution of CD36 to the pathogenesis of insulin resistance in adipose tissue. The roles of CD36 in the reduction of adipose tissue insulin sensitivity with increased lipolysis are to promote inflammation and promote remodeling of the adipose tissue with hypertrophy of adipocytes, and an adverse profile of adipokines mediated by oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL) and advanced glycation end product (AGE). Ultimately, this leads to a significant release of fatty acids (FAs) and an increase in free fatty acid (FFA) concentration in plasma, exceeding the energy needs of such organs as the liver, muscle, and heart.