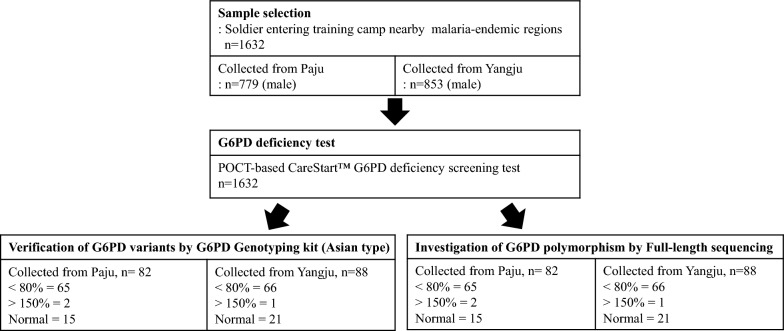
Fig. 1.
Schematic diagram of sample selection for enzymatic and genetic evaluation of G6PD deficiency. In accordance with IRB-approved (AFMC-17-IRB-023) protocol, blood samples were collected from soldiers who agreed to participate in the study. All 1632 blood samples were collected in two cities, Yangju (n = 853) and Paju (n = 779) and were screened using the CareStart G6PD and Hb POC test. Based on screened results, 134 samples that were below (30–80%; n = 131) and above (> 150%; n = 3) the G6PD median value underwent genetic analysis using a G6PD genotyping kit and full-length sequencing. Thirty-six normal-range G6PD samples were also tested. Paju recruitment training camp: n = 779/1007, consent rate = 77%; Yangju recruitment training camp: n = 853/1011, consent rate = 84%