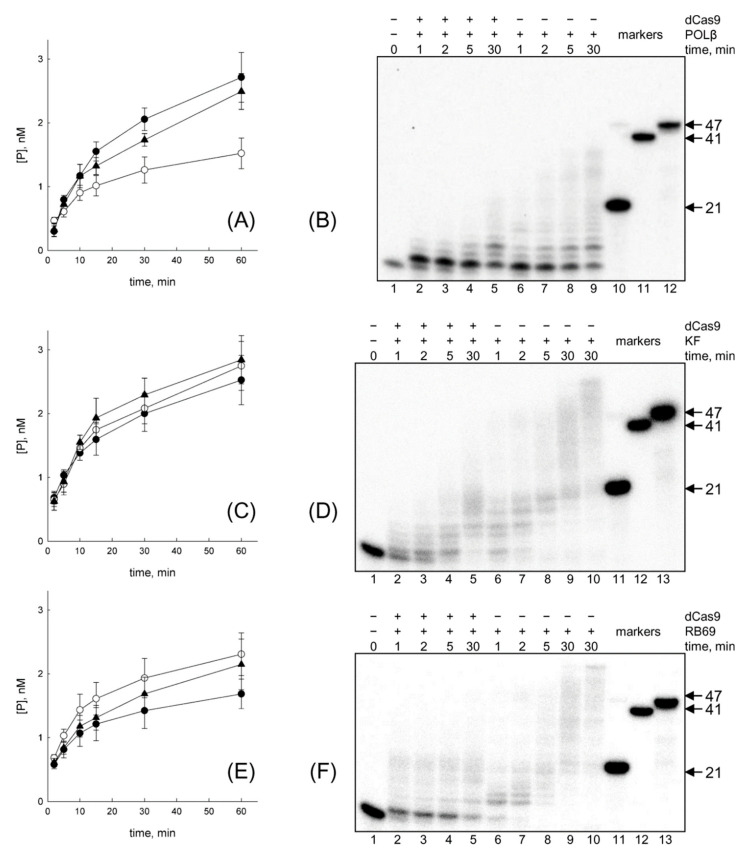
Figure 8.
Displacement of Cas9 by DNA polymerases. (A) POLβ interacting with Cas9 bound to DNA; (B) primer extension by POLβ in the presence of dCas9; (C) KF interacting with Cas9 bound to DNA; (D) primer extension by KF in the presence of Cas9; (E) RB69 DNA polymerase interacting with Cas9 bound to DNA; (F) Primer extension by RB69 DNA polymerase in the presence of dCas9. In (A,C,E) white circles show the secondary substrate cleavage in the absence of a DNA polymerase, black circles, in the presence of a DNA polymerase and dNTPs and black triangles, in the presence of KF without dNTPs. Mean ± SEM of 3–5 independent experiments are presented. In (B,D,F) lane 1 is DNA substrate (primer/template/downstream strand, primer length 11 nt) without dCas9 or polymerase; lanes 2–5, DNA polymerase and dCas9 are present; lanes 6–9, only DNA polymerase is present; lane 10 in (D,F) DNA polymerase extending the primer/template construct without a downstream strand (absent from (A) since POLβ has very low activity without a downstream strand); lanes 11–13 (10–12 in (A)) mobility markers with their positions indicated by the arrows.