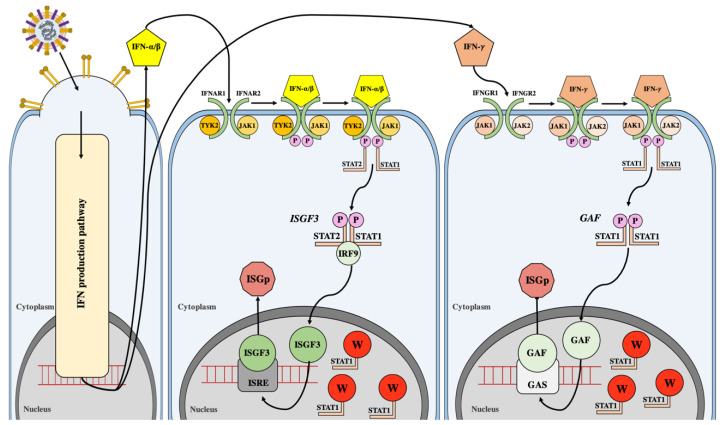
Figure 4.
IFN signalling pathway and production of IFN-stimulated gene (ISG) products. Virus-mediated induction of the type I IFN production activates IFN signalling pathways. Type I IFNs (IFNα/β) bind cognate IFNAR receptors that activate Janus kinase (JAK) proteins JAK1 and TYK2. When activated, JAKs phosphorylate STATs. The activated STAT-1 and STAT-2 proteins form heterodimers that associate with IRF-9, creating the ISGF3 complex. ISGF3 associates with coactivators to induce the expression of genes downstream of promoters with IFN-stimulated response elements (ISREs). This upregulates many host antiviral products (ISGp). Type II interferon (IFN-γ) binds IFNGR receptors to stimulate JAK activity and phosphorylation of STAT-1 homodimers (GAF complex). GAF binds promoters of gamma-activated sequences (GAS)-associated genes that upregulate host antiviral products (ISGp). W protein binds and sequesters unphosphorylated STAT in the nucleus as a high molecular weight complex, antagonizing the function of STAT in the JAK-STAT pathway.