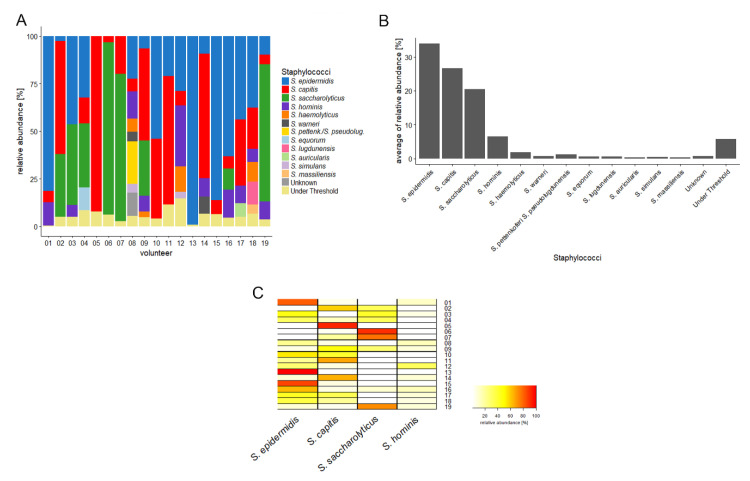
Figure 1.
Diversity and abundance of staphylococcal species in back skin samples, based on amplicon next generation sequencing (NGS) data. (A) Relative abundance of staphylococcal species for each volunteer (n = 19). Twelve staphylococcal species were identified in the cohort using the tuf amplicon-NGS approach. The four most abundant species in the cohort were Staphylococcus epidermidis (in blue), Staphylococcus capitis (in red), Staphylococcus saccharolyticus (in green) and Staphylococcus hominis (in purple). (B) The average relative abundance of the identified 12 staphylococcal species is shown; S. epidermidis was detected with an average abundance of 34.0%, S. capitis with 26.6%, S. saccharolyticus with 20.5%, and S. hominis with 6.5%. (C) The relative abundance of the four most prevalent staphylococcal species is shown for each back skin sample in a heat map. S. epidermidis was detected in four samples with a very high abundance (>60% of all reads); S. capitis and S. saccharolyticus were detected with such a high abundance in three samples each.