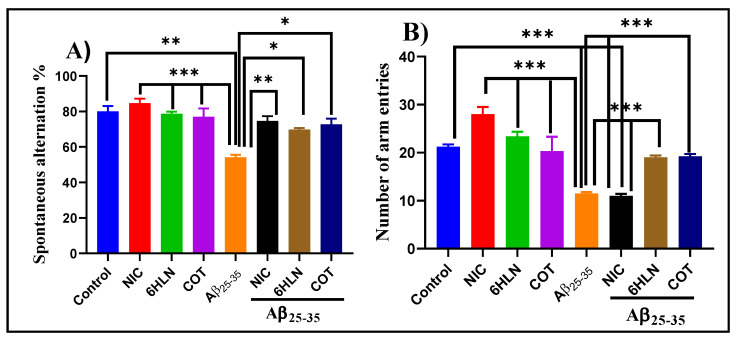
Figure 4.
Effects of NIC, 6HLN and COT (0.3 mg/kg, b.w., i.p.) administration in Aβ25-35-treated rats on (A) spontaneous alternation percentage and (B) the number of arm entries in the Y-maze task. Values are expressed as means ± S.E.M. (n = 6 animals per group). ANOVA analysis identified overall significant differences between groups in (A) F(4,10) = 16.5, p < 0.0002 and (B) F(4,15) = 130.8, p < 0.0001. For Tukey’s post hoc analyses–(A) ** Control vs. Aβ25-35, *** NIC vs. Aβ25-35, 6HLN vs. Aβ25-35, COT vs. Aβ25-35: p < 0.0001, ** Aβ25-35 vs. NIC + Aβ25-35: p < 0.001, * Aβ25-35 vs. 6HLN + Aβ25-35, Aβ25-35 vs. COT + Aβ25-35: p < 0.01; (B)*** Control vs. Aβ25-35, Control vs. NIC + Aβ25-35, NIC vs. Aβ25-35, 6HLN vs. Aβ25-35, COT vs. Aβ25-35, Aβ25-35 vs. 6HLN + Aβ25-35, NIC + Aβ25-35 vs. 6HLN + Aβ25-35, Aβ25-35 vs. COT + Aβ25-35, NIC + Aβ25-35 vs. COT + Aβ25-35: p < 0.0001.