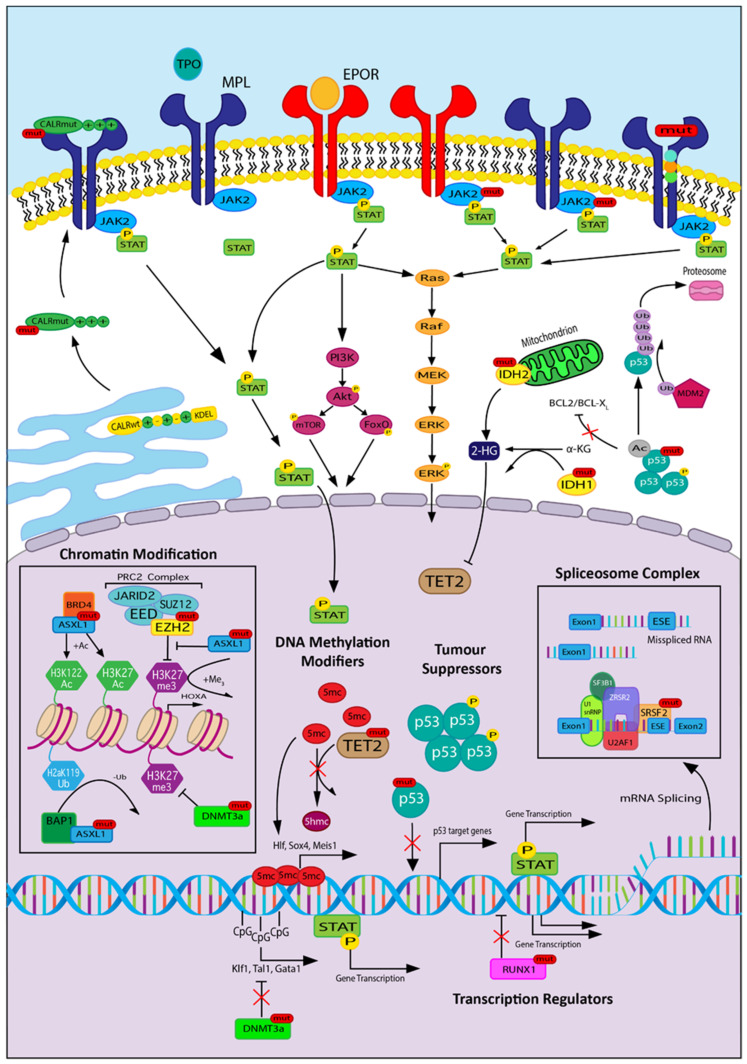
Figure 2.
The molecular signalling pathways involved in MPN: The cell surface receptors are erythropoietin receptor (EPOR; red) and thrombopoietin receptor/MPL (navy blue), MPL with mutated Calreticulin (CALR), wildtype MPL with no ligand (thrombopoietin (TPO)) bound and no STAT signalling, wildtype EPOR with bound ligand (erythropoietin (EPO)) leading to STAT signalling, EPOR with JAK2 mutant, MPL with JAK2 mutant and mutated MPL. The cytoplasm shows STAT pathway signalling with activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt and RAS pathways, and the nucleus (lilac background) shows the effects of driver and coexisting mutations on nuclear functions. Headings for DNA methylation modifiers, tumour suppressors, transcription regulators, spliceosome complex and chromatin modification identify the key sites of coexisting mutations. Abbreviations not mentioned in the body of the article: STAT, signal transducers and activators of transcription; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; Akt, Protein kinase B; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; SUZ12, suppressor of zeste 12 homolog; EEZ, embryonic ectoderm development; BAP1, BRCA1-associated protein 1; BRD4, bromodomain containing protein 4; BCL-2, B cell lymphoma 2; BCL-XL, B cell lymphoma extra large; Ac, acetylated; Me, methylated; Ub, ubiquitinated; P, phosphorylated; mut, mutated.