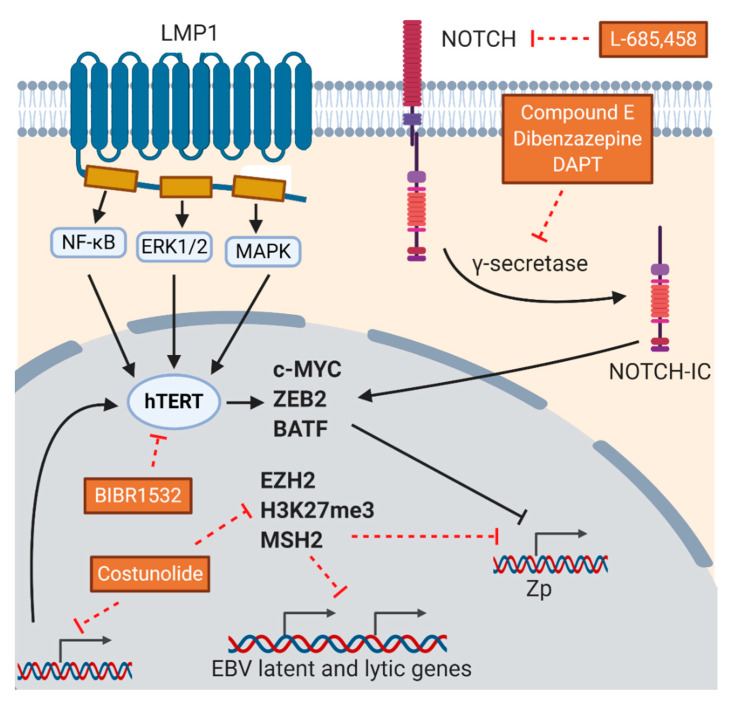
Figure 5.
Relationship between EBV proteins, hTERT, and NOTCH signaling pathway and the modes of action of compounds with lytic induction potentials. hTERT inhibits the expression of BZLF1 through the NOTCH2/BATF pathway. EBNA2 is regarded as the functional homolog of active NOTCH intracellular domain (Notch-IC) and LMP2A can activate the NOTCH pathway. NOTCH2 inhibits the reactivation of lytic cycle of EBV through the upregulation of Zeb2 by NOTCH-IC, a transcription factor that represses BZLF1 transcription. γ-secretase inhibitors such as compound E and dibenzazepine can reactivate lytic cycle of EBV by preventing the release of Notch-IC. Other compounds that may reactivate the lytic cycle include hTERT inhibitor, BIBR1532, which selectively inhibits telomerase activity, and another γ-secretase inhibitor, DAPT.