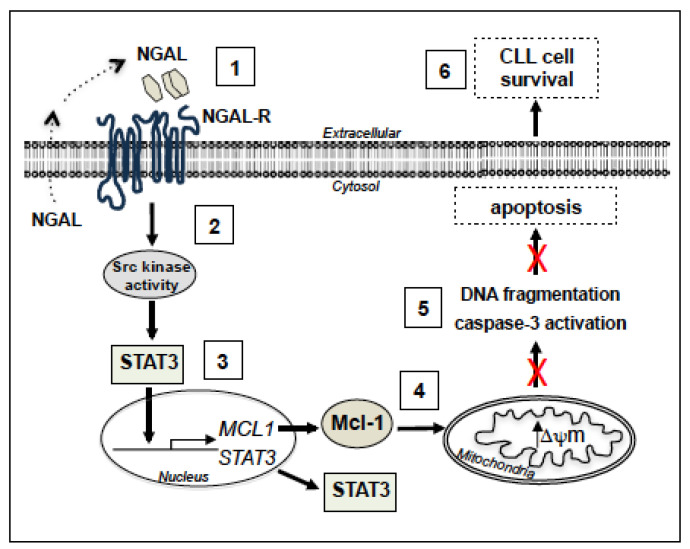
Figure 8.
Putative model for the involvement of cell signaling pathways in the induction of survival by NGAL in CLL cells. By binding to surface NGAL-R (1), NGAL (dimers and monomers) likely leads to the activation of an Src family kinase (2), which, in turn, activates STAT3. STAT3 dimer enters the nucleus and binds the promoters of STAT3 and MCL1 (3). Following STAT3 and MCL1 transcription, STAT3 and Mcl-1 proteins accumulate in the cytoplasm, and Mcl-1 exerts its anti-apoptotic activity by preventing mitochondrial depolarization (4), leading to the inhibition of caspase-3 activation and DNA fragmentation (5), ultimately favoring cell resistance to apoptosis (6). The dotted arrow suggests an autocrine NGAL stimulation loop for CLL cell survival.