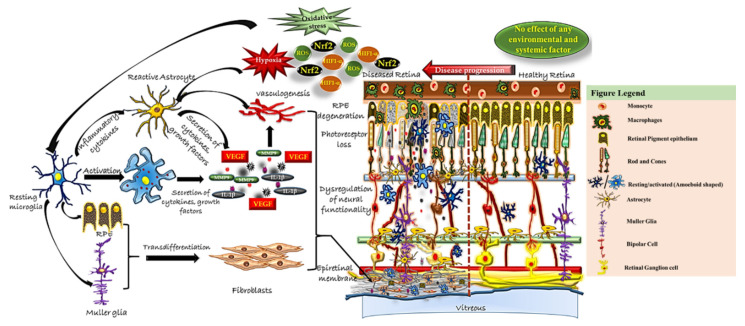
Figure 8.
Schematic representation of proposed microglial activity in the epiretinal membrane of the retina. In healthy retina, resident microglia are involved in immune surveillance of all the layers of the retina and maintain retinal homeostatis by synaptic pruning, regulation of neurogenesis and axonal growth. With their phenotypic change of shape, they phagocytose cellular debris. Different kinds of stress/insults lead to abnormal functioning of retinal neurons, microglia, astrocyte, Müller glia and RPE cells. The resident/resting microglia in the retina get activated by transforming into an amoeboid shape and further interact with other neighboring retinal cells, causing abnormal functioning and trans-differentiation into proliferative cells types [10,11]. It also induces the secretion of several chemokines, proinflammatory cytokines and growth factors etc (results from the present study) that could aid in membrane formation by remodeling of the extracellular matrix proteins in retina and thereby contribute to disease pathogenesis.