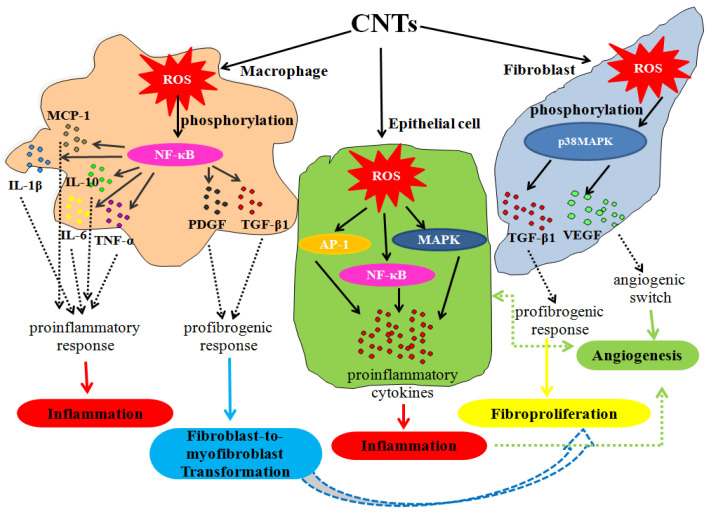
Figure 5.
Cell signaling events induced by CNTs, original figure. In different cell types, CNTs induce reactive oxygen species (ROS)-dependent activation of certain cell signaling pathways (NF-κB, MAPK, AP-1), and subsequently, secretion of proinflammatory cytokines (in macrophages and epithelial cells) or profibrogenic and angiogenic factors (in macrophages and lung fibroblasts). Proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, IL-10, TNF-α, MCP-1) are responsible for inflammation, profibrogenic factors (TGF-β1, PDGF) cause fibroproliferation and differentiation of fibroblast to myofibroblast, while growth factor (VEGF), as well as proinflammatory cytokines, initiates angiogenesis. (NF-nuclear factor, MAPK-mitogen-activated protein kinase, AP-activator protein, IL-interleukine, TNF-tumour necrosis factor, MCP-monocyte chemoattractant protein, TGF-transforming growth factor, PDGF-platelet-derived growth factor, VEGF-vascular endothelial growth factor).