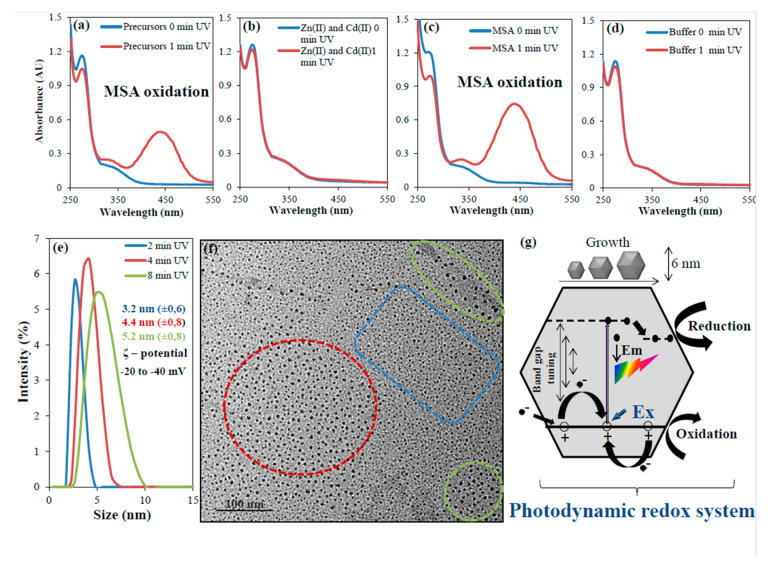
Figure 1.
Monitoring of behavior of individual components of the precursor mixture. UV/Vis absorption spectra of tetrazolium salt producing a formazan dye upon reduction by a superoxide anion generated by photodissociation (photo-oxidation) of thiols (MSA) before (blue) and after (red) 1 min UV irradiation, the sample consisted from precursors (a) Zn(II), Cd(II) and MSA in pH 7 controlled by phosphate buffer, (b) Zn(II), Cd(II) in phosphate buffer pH 7, (c) solution of MSA in phosphate buffer pH 7 and (d) phosphate buffer pH 7 solution. QDs (quantum dots) characterization according to (e) size distribution of ZnCd QDs in range 3–5 nm after 2 (blue), 4 (red) and 8 (green) min UV irradiation and respective zeta potential in range the −20 to −40 mV, (f) Transmission electron micrograph of ZnCd QDs after 8 min UV irradiation of precursors (Zn:Cd:MSA in phosphate buffer pH 7), scale bar represents 100 nm. (g) Schematic representation of the proposed photodynamic redox system. Excited electrons (-) have a strong reduction potential and holes (+) are very strong oxidizing agents. Oxidation-reducing properties of ZnCd QDs can be significantly changed according to the band gap distance () associated with growing of QDs.