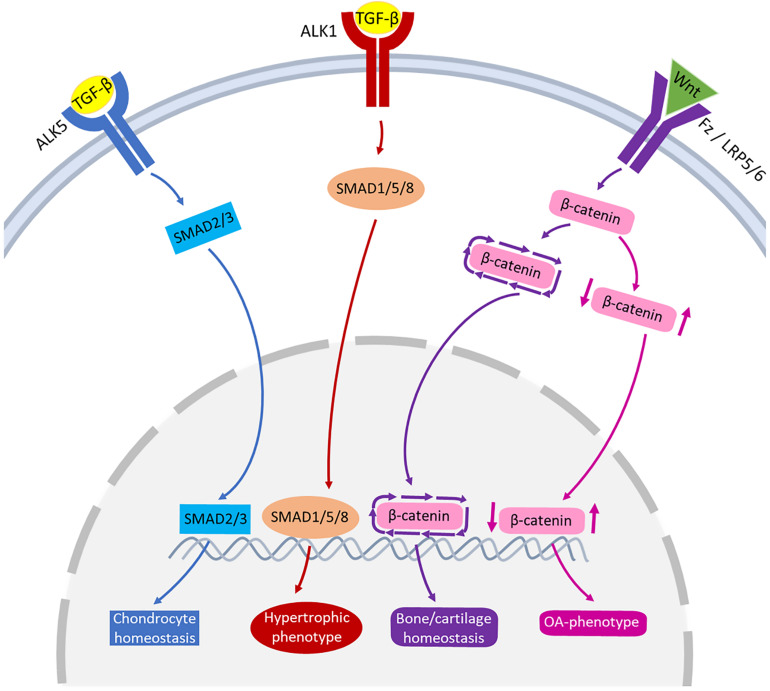
FIGURE 3.
Schematic representation of the signaling pathways of TGF-β and Wnt involved in joint pathophysiology. TGF-β can bind to ALK5, that activates SMAD2/3 leading to chondrocyte homeostasis (blue pathway arrows). TGF-β can also bind to ALK1, activating SMAD1/5/8 that may lead to hypertrophic phenotype of chondrocytes (red pathway arrows). Wnt binds to receptors Fz or LRP5/6 activating β-catenin synthesis. A healthy expression of β-catenin leads to bone/cartilage homeostasis (purple pathway arrows) while imbalanced β-catenin can result in an OA-phenotype (pink pathway arrows).