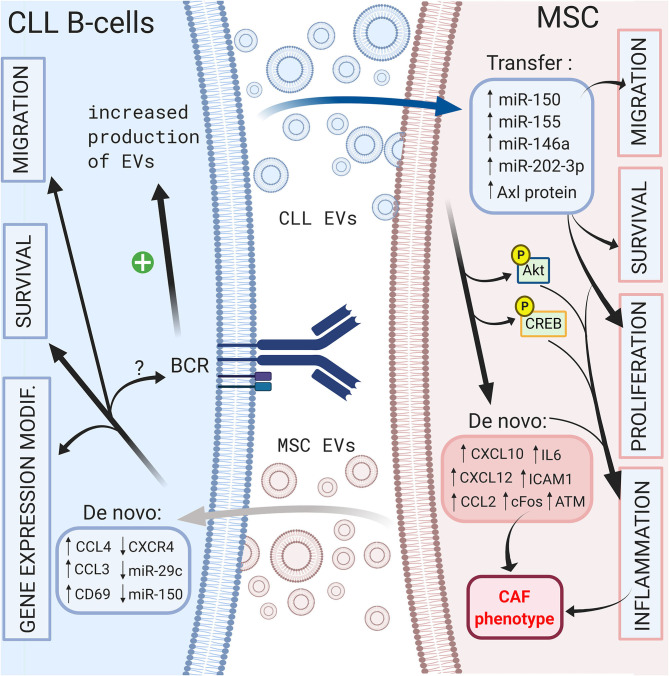
Figure 4.
Crosstalk between CLL B-cells and MSCs via extracellular vesicles. Bi-directional communication exists between CLL B-cells and MSCs via the production of extracellular vesicles by both cell types. MSC EVs increase the migration, the survival of CLL B-cells and change their gene expression profile (138). CLL B-cells derived EVs can transfer microRNA (135, 144, 145) or protein (143) leading to the migration, the survival and the proliferation of MSCs (135). In addition, they induce an inflammatory phenotype in stromal cells resulting into a cancer-associated fibroblast (CAF)-phenotype (135). Interestingly BCR stimulation increases the production of CLL EVs (145). Figure created with BioRender.com.