Figure 5.
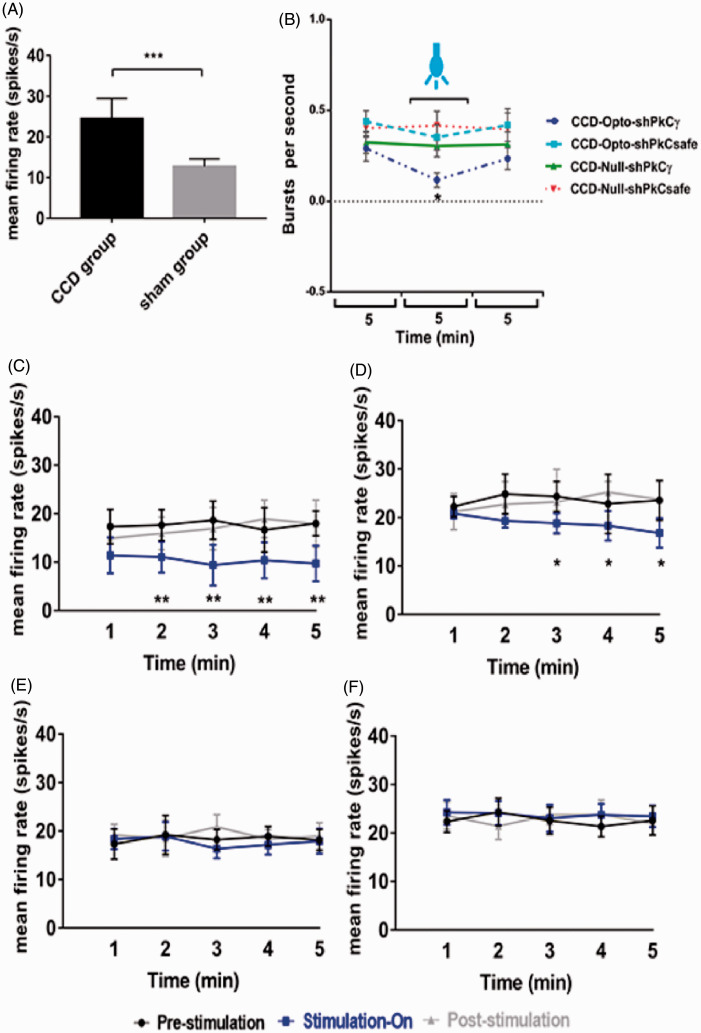
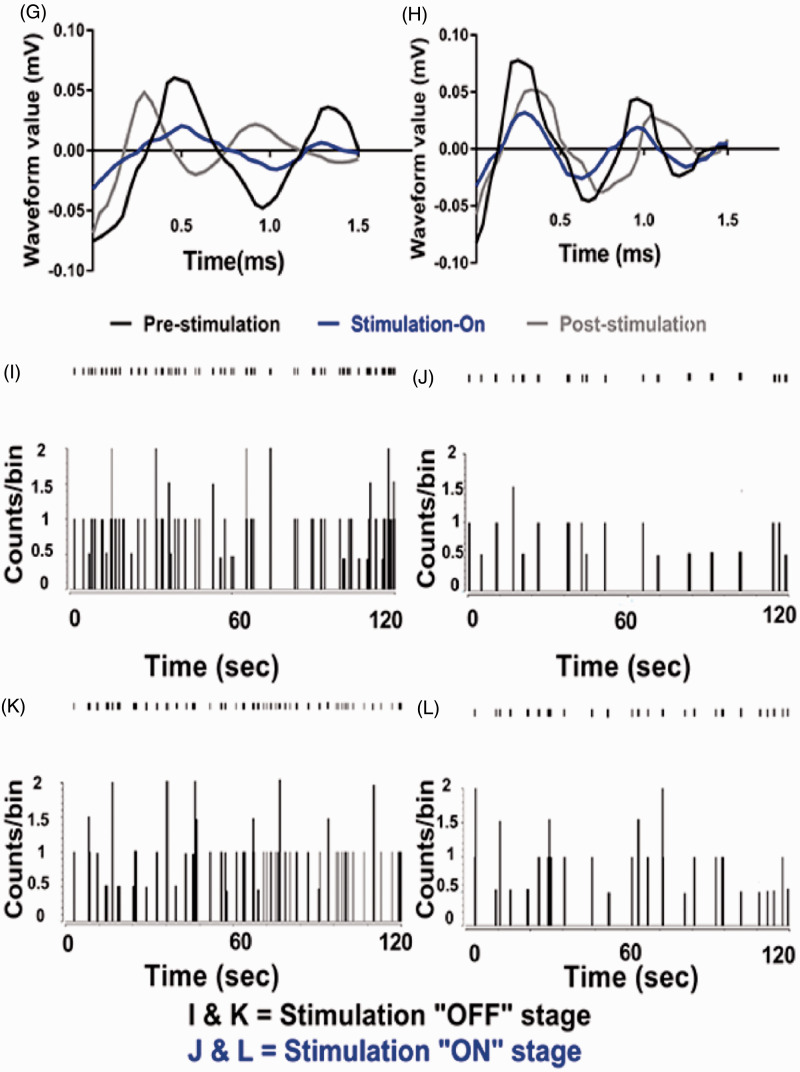
Electrophysiology results of thalamic output by optic stimulation in motor cortex. (A) Evoked firing rates in the neurons of VPL thalamus of CCD animals compared to sham-operated animals. Unpaired t-test was used to compare between sham group and CCD group. (B) Burst firing rates of CCD-grouped animals following optical stimulation. Significant change was seen in only CCD-Opto-shPKCγ group. Burst rates decreased in CCD-Opto-shPKCsafe group also, but it was not significant. (C, D) In vivo recording of CCD-Opto-shPKCγ-grouped animals (C) and CCD-Opto-shPKCsafe-grouped animals (D) from the VPL thalamus. Firing output (spikes/s) declines under blue laser stimulation, which is higher in the pre- and post-light states. (E, F) No changes of firing rates in CCD-Null-shPKCγ and CCD-Null-shPKCsafe group, respectively. Two-way ANOVA test was used to compare neuronal activity according to the optical stimulation. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p<0.001 significant difference between the indicated values (ANOVA). (G) Average action potential waveform of VPL neuron of CCD-Opto-shPKCγ-grouped animal. (H) Average action potential waveform of CCD-Opto-shPKCsafe-grouped animal. (G, H) In both cases, amplitude got decreased during optical stimulation on motor cortex. (I, J) Perievent raster histogram of responses of CCD-Opto-shPKCγ-grouped animal’s VPL neurons. (K, L) Raster plot responses of CCD-Opto-shPKCsafe-grouped animal’s VPL neurons. (I, K) Increased firing response when there is no optical stimulation present. (J, L) During optical stimulation, VPL firing response got decreased. Bin size = 50 ms.
CCD: chronic compression of dorsal root ganglion; PKCγ: protein kinase C gamma.