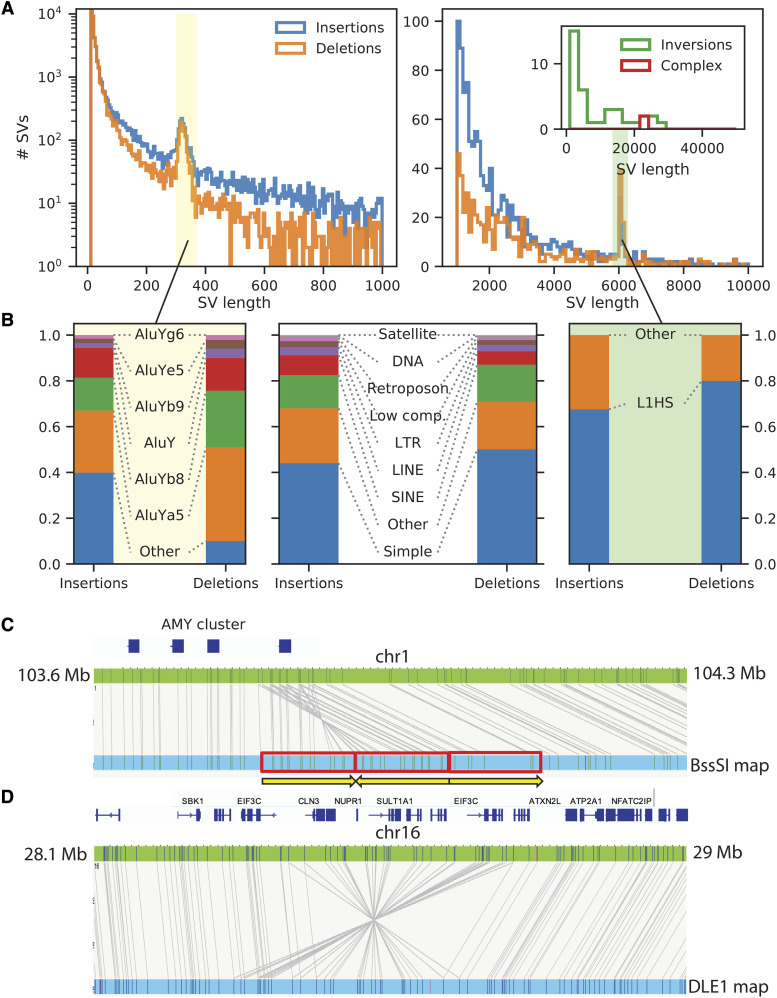
Figure 7.
Structural variation between the WI-38 and the reference genome (GRCh38). (A) Length distributions of structural variants. WI-38 SVs were compared of the GRCh38 reference genome and the histograms of lengths of insertions (blue), deletions (orange), inversions (green) and complex SVs (red) are shown. As expected, SVs of ∼300 bp were mostly comprised of AluY TEs (B, left panel) and those of ∼6 kb were highly enriched with L1HS TEs (B, right panel). (B) Structural variants were highly enriched with repeats and transposable elements. Bar charts showing repeat type compositions of SVs. Left panel – when focusing on SVs of ∼300 bp (Other – non-AluY), Right panel – when focusing on SVs of ∼6 kb (Other – non-LINE). Central panel – all SVs (Other – non-repeats). (C, D) Bionano optical maps provide additional interpretation of structural variants. Examples of structural variants identified by in hybrid assembly as “complex” and by interpreted by Bionano optical as inverted duplication (C) and inversion (D). Complex rearrangement on Chromosome 16. Alignment of the DLE-1 optical map (blue) shows a large SV relative to GRCh38 (green).