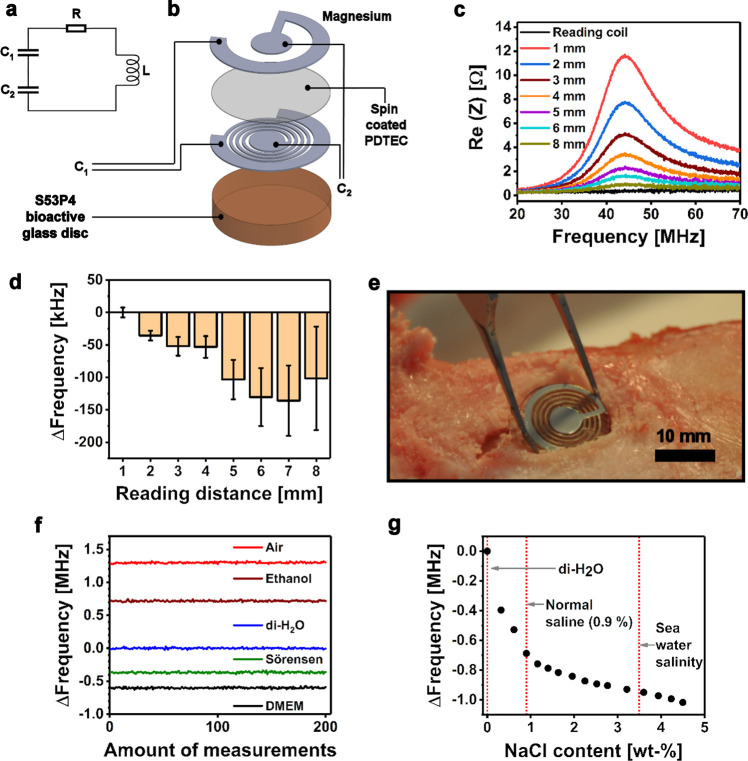
Figure 2.
(a) A simplified lumped element model and (b) schematic structure of the bioactive glass-based resonance sensor. (c) Illustration of the resonance peaks at varying reading distances. (d) Effect of reading distance onto the resonance frequency (∼44 MHz). The results are presented relative to the reading distance of 1 mm and given as mean ± standard deviation (n = 100). (e) An envisioned application of the sensor as a sensor-containing bone graft disc shown in a cadaveric porcine tibia. (f) Relative resonance frequency behavior of a parylene-coated sensor embedded in different media, where the mean of 200 measurements in deionized water (di-H2O) has been set as the zero point. (g) Effect of increasing NaCl content in the resonance frequency of the coated sensor embedded in di-H2O.