Fig. 2. Dscam KD prevents delamination of newborn neurons.
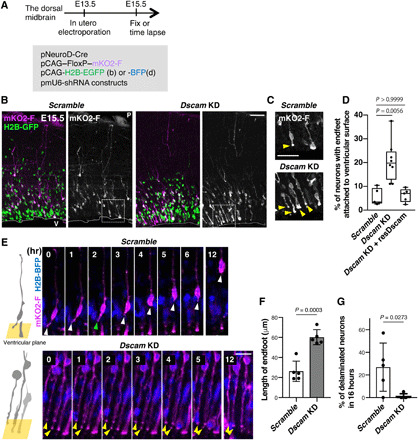
(A to F) Embryonic dorsal midbrains were electroporated in utero at E13.5 with Cre-loxP–based neuron labeling. pCAG-H2B-EGFP (B) or BFP (D) plasmid was introduced to monitor nuclear position. At E15.5, midbrain coronal slices were analyzed. (A) Experimental design. (B) E15.5 dorsal midbrain coronal sections expressing mKO2-F and H2B-EGFP in electroporated cells with control (scramble) or Dscam KD. Higher magnification in (C) represents areas surrounded by dotted boxes. P, pia; V, ventricle. Scale bar, 50 μm. (C) Excessive abnormal apical processes (yellow arrowheads) observed in Dscam KD condition. Scale bar, 20 μm. (D) Percentage of neurons (mKO2-F–positive cells) with endfeet attached to the ventricular surface. Box plots show median (horizontal line), quartiles (box), and range (whiskers) from five to eight brains; Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple comparisons test. (E) Endfeet live imaging in slice culture. Left-side cartoons represent the angle of the ventricular surface in each movie. Each frame comprises z-stacked images. Control mKO2-F–positive neurons had apical endfeet (white arrowhead) first, which were then retracted (green arrowhead). In Dscam KD neurons, most mKO2-F–positive neurons bore long endfeet (yellow arrowheads). The ventricle is toward the bottom. Scale bar, 30 μm. (F) Length of mKO2-F–positive endfeet (Scramble, n = 5; Dscam-KD, n = 5). (G) Ratio of mKO2-F–positive delaminating neurons in 16 hours (Scramble, n = 5; Dscam KD, n = 5). Data are presented as the mean ± SEM; unpaired two-tailed t test.
