Fig. 3. Dscam KD prevents neuronal migration and isolated behavior.
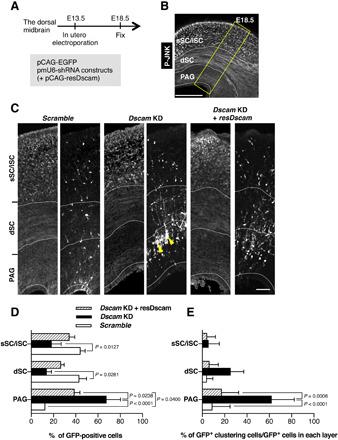
(A to E) Dorsal midbrains were electroporated in utero at E13.5 with plasmids encoding pCAG-EGFP and indicated shRNA constructs and pCAG vector encoding shRNA-resistant expression construct (resDscam). At E18.5, midbrain coronal slices were analyzed. (A) Experimental design for in utero electroporation and analyses. (B) Schematic of coronal section of the dorsal midbrain at E18.5. Slices were stained with anti–phospho-JNK (P-JNK) antibody, a marker that demarcates the sSC/iSC, dSC, and PAG layers in the dorsal midbrain. Yellow box indicates the area shown in (C). Scale bar, 300 μm. (C) E18.5 dorsal midbrain coronal sections expressing EGFP in the electroporated cells with shRNA vectors and pCAG vector coding resDscam. Yellow arrowheads indicate impaired neuronal migration and abnormal cell clustering. Scale bar, 50 μm. (D) Distribution of EGFP-positive cells in three layers demarcated by anti–phospho-JNK antibody (Scramble, n = 4; Dscam KD, n = 4; Dscam KD and resDscam, n = 4). (E) Ratios of abnormal cell cluster formation in each layer (Scramble, n = 4; Dscam KD, n = 4; Dscam KD and resDscam, n = 4). Data are presented as the mean ± SEM; two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey’s multiple comparison test.
