Fig. 6. PKA is centrosomal, and its delocalization phenocopies cilium ablation.
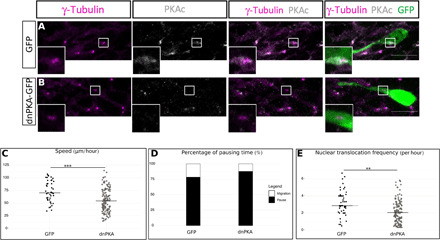
(A) Immunocytochemistry of a GFP-positive neuron showing PKAc subcellular localization (gray) around γ-tubulin–positive centrosome (magenta) (N = 3, n = 43). Scale bar: 10 μm. (B) Immunocytochemistry of a dnPKA-GFP–positive neuron showing a delocalization of PKAc (gray) from the γ-tubulin–labeled centrosome (magenta) (N = 2, n = 30). Scale bar: 10 μm. (C) Speed of neurons electroporated with GFP or dnPKA-GFP in Kif3alox/lox background. GFP: 75.49 ± 3.48 μm/hour; dnPKA: 55.76 ± 1.90 μm/hour [one-way ANOVA (F4,383 = 7.87, P < 0.001), followed by Tukey post hoc test (***P < 0.001)]. (D) Percentage of pausing time of neurons electroporated with GFP or dnPKA-GFP in Kif3alox/lox background. GFP: 76%; dnPKA: 86% (Pearson’s χ2 test = 67.25, P < 0.001). (E) NK frequency of neurons electroporated with GFP or dnPKA-GFP in Kif3alox/lox background. GFP: 3.15 ± 0.21 NK/hour; dnPKA: 2.23 ± 0.12 NK/hour [one-way Kruskal-Wallis (χ2 = 19.57, P < 0.001, df = 4), followed by Nemenyi (***P < 0.001)]. The black line represents the median. GFP: N = 3, n = 48; dnPKA: N = 3, n = 146. **P < 0.01.
