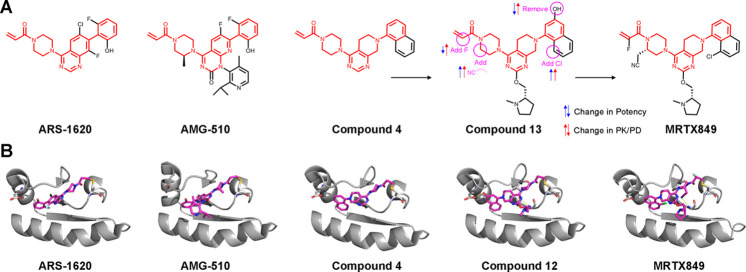
Figure 1.
Structures and optimization of clinical covalent KRASG12C inhibitors. (A) Chemical structures of advanced KRASG12C inhibitors. Highlighted in red is the almost identical scaffold shared by all three major series. Compound 4 previously reported by Fell et al.5 was progressed to compound 13 that suffered from clearance problems. Now, compound 13 was optimized to the clinical compound MRTX849. Red and blue arrows indicate improvement or deterioration in potency and PK/PD, respectively, for each modification introduced. (B) Cocrystal structures of KRASG12C in complex with the various binders show the highly similar binding modes of these compounds. No structure is available for compound 13; however a very close analog (compound 12(5)) illustrates the changes in interactions with the protein achieved by the introduced modifications. PDB codes from left to right are the following: 5V9U, 6OIM, 6N2J, 6N2K, 6UT0.