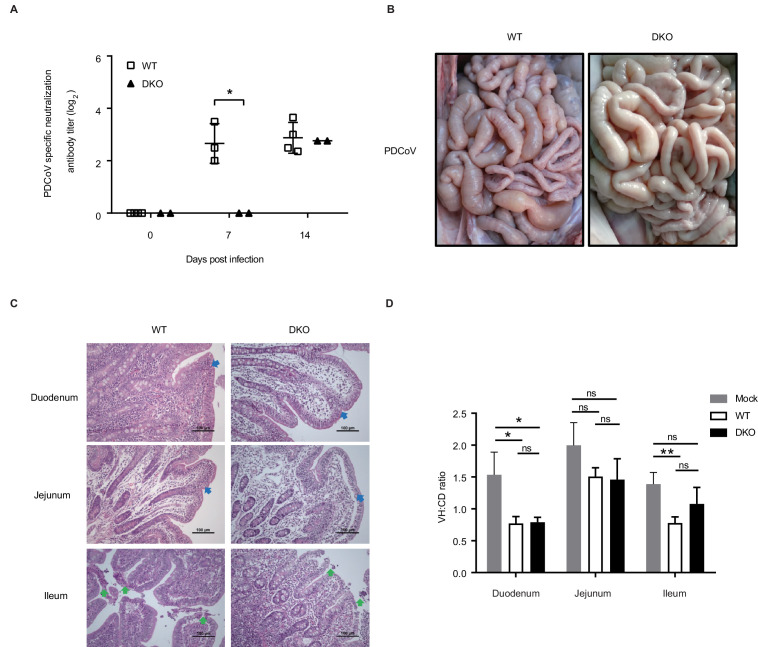
Figure 4. DKO pigs exhibit reduced susceptibility to PDCoV.
(A) PDCoV-specific antibody detection in serum from both WT and DKO pigs at 0, 7, and 14 dpi. WT group: 0 dpi, N = 4; 7 dpi, N = 3; 14 dpi, N = 4. DKO group, N = 2. (B) Representative macroscopic lesions of the small intestines at 14 dpi from WT and DKO groups of pigs challenged with PDCoV. (C) H and E staining of small intestine segments sections to detect lesions; small intestine tissues were derived from PDCoV-infected WT and DKO pigs. Intestinal villi fusion, infiltration of lymphocytes in the intestinal mucosa, and a large number in the intrinsic membrane (blue arrow), and necrosis and shedding of intestinal mucosal intraepithelial cells and naked lamina propria (green arrow). (D) The ratio of intestinal villus height to the crypt depth derived from both WT and DKO pigs at 14 dpi. Mock: duodenum to ileum, N = 3. WT: duodenum to ileum, N = 3. DKO: duodenum to ileum, N = 3. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD. Statistical significance was determined by Student’s t-test; ns, p>0.05; *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001.