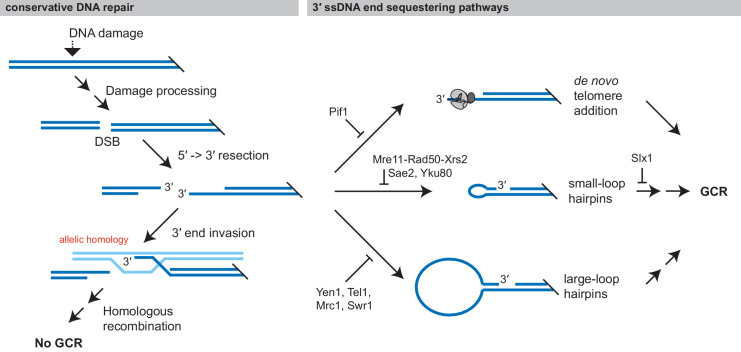
Figure 11. Formation of GCRs is promoted by sequestering 3' ssDNA ends.
Conservative repair of many types of DNA damage involves processing the DNA damage to yield a DSB, which is then resected and undergoes allelic HR with the sister chromatid. Allelic HR requires that the 3' ssDNA ends of the DSB are available to initiate HR. GCRs form when intermediates in conservative repair are acted on by competing DNA processing pathways, particularly if these pathways sequester the 3' ssDNA end from allelic HR. Analysis of the structure of GCRs, including the analysis presented here has identified three major 3' ssDNA sequestering pathways, which are suppressed by distinct gene products: de novo telomere addition, formation of small-loop ssDNA hairpins, and formation of large-loop ssDNA hairpins.