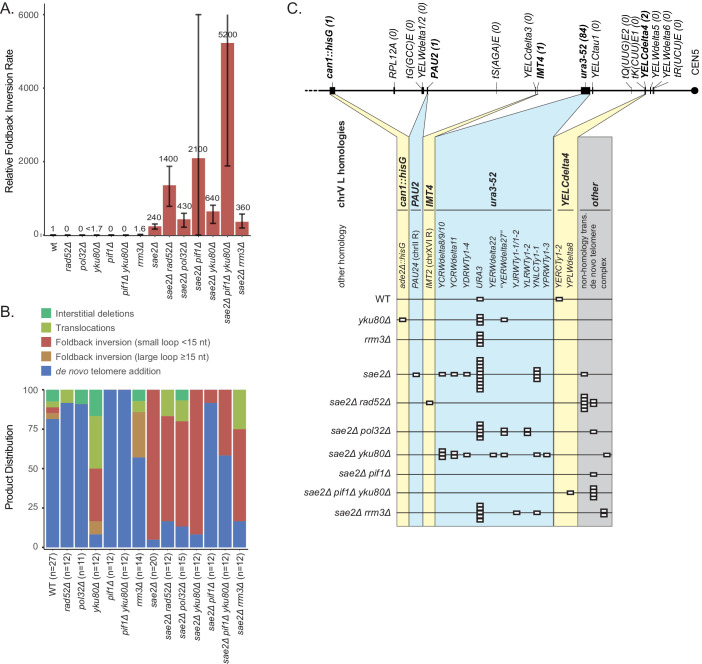
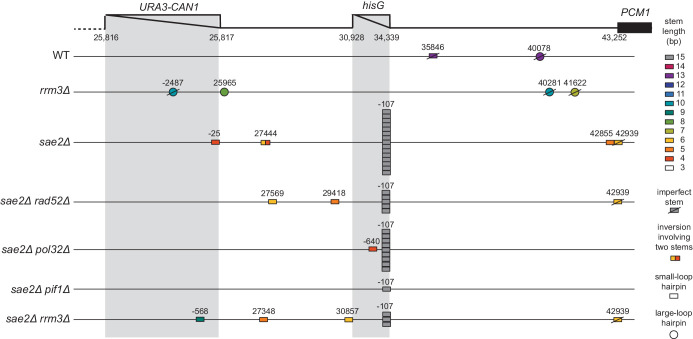
Figure 9. Analysis of GCRs generated in strains with mutations in genes that have potential roles in recombination and BIR.
(A) Comparison of the foldback inversion GCR rates relative to wild-type; the foldback inversion rate reported for the yku80Δ mutant is the upper bound estimated from the fluctuation results. (B) Comparison of the observed GCR spectra. (C) Distribution of foldback inversion resolution products observed by genotype. Yellow and blue backgrounds distinguish homologies on chrV L involved in the rearrangement, and columns indicate homologies involved in other regions of the genome. Grey background indicates either non-homology-mediated resolution products or those involving multiple steps, ‘complex’.