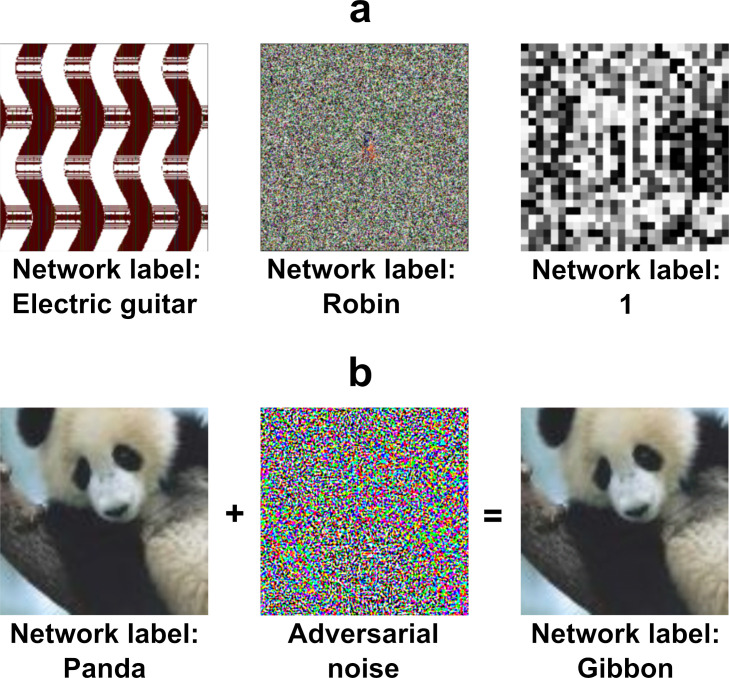
Figure 1. Examples of two types of adversarial images.
(a) fooling adversarial images taken from Nguyen et al., 2015 that do not look like any familiar object. The two images on the left (labelled ‘Electric guitar’ and ‘Robin’) have been generated using evolutionary algorithms using indirect and direct encoding, respectively, and classified confidently by a DCNN trained on ImageNet. The image on the right (labelled ‘1’) is also generated using an evolutionary algorithm using direct encoding and it is classified confidently by a DCNN trained on MNIST. (b) An example of a naturalistic adversarial image taken from Goodfellow et al., 2014 that is generated by perturbing a naturalistic image on the left (classified as ‘Panda’) with a high-frequency noise mask (middle) and confidently (mis)classified by a DCNN (as a ‘Gibbon’).