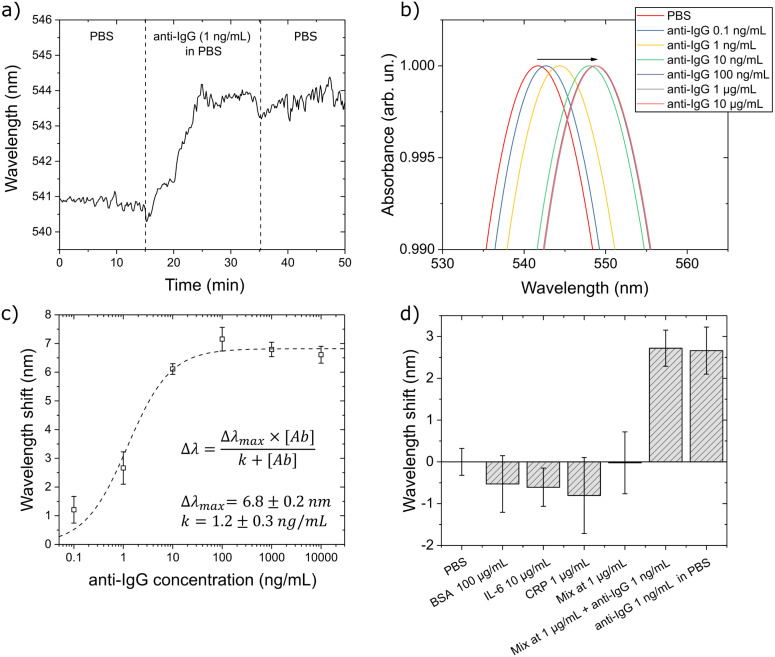
Fig. 4.
LSPR response for an IgG/anti-IgG model system in the opto-microfluidic platform. (a) Typical sensorgram corresponding to the detection of 1ng/mL of IgG antibody in PBS. The vertical dashed lines highlight each step of the protocol described in the text. (b) Absorption spectra of the functionalized gold nanospikes upon exposure to IgG antibody at varying concentrations. The antigen–antibody binding occurring on the surface of the Au nanospikes increases the local RI, causing the red shift of the LSPR peak position (see the black arrow). (c) LSPR response at different IgG antibody concentrations. Each data point corresponds to averaged data from triplicate experiments, with the error bars denoting the standard deviation. (d) Specificity test against BSA (/mL), IL-6 (/mL), CRP (/mL) and a mixture of these analytes at /mL. All these samples produce negligible wavelength shifts falling under the experimental error. However, when 1ng/mL of anti-IgG is added to the mixture, the wavelength shift is similar to that measured in the PBS with 1ng/mL of anti-IgG.