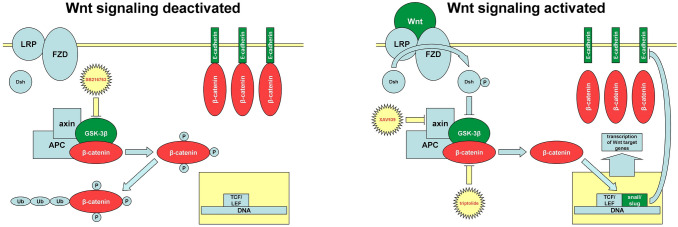
Fig. 1.
Canonical Wnt signaling pathway: In absence of Wnt ligand (left), the destruction complex, consisting of GSK-3β, adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) and axin, hyperphosphorylates β-catenin, which marks it for ubiquitination (Ub) and proteasomal degradation. Binding of Wnt ligand (right) to a frizzled (FZD)/lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP) receptor complex leads to the phosphorylation of dishevelled (Dsh) inactivating GSK-3β and preventing the phosphorylation of β-catenin. Non-phosphorylated β-catenin shifts into the nucleus and forms a complex with T-cell factor (TCF)/lymphoid enhancer factor (LEF) activating transcription of Wnt target genes. Furthermore, the expression of zinc-finger transcription factors snail and slug is upregulated. They bind to E-boxes in E-cadherins promoter region and prevent its transcription. Suppresion of E-cadherin offers more available cytoplasmic β-catenin and induces a self-driven positive feedback loop. In conclusion, by losing E-cadherin as an adhesion molecule cells undergo EMT (Arend et al. 2013; Gasior et al. 2017; Gatcliffe et al. 2008). The three inhibitors (SB216763, XAV939 triptolide) used in this study, are shown in their typical domain