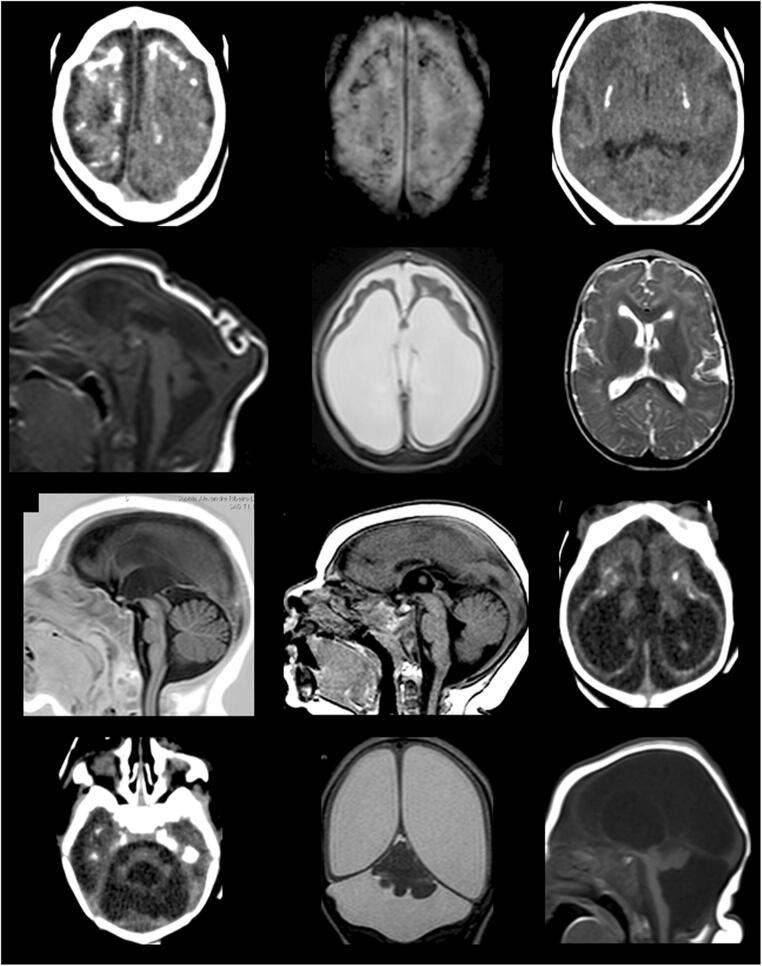
Fig. 1.
Brain images of infants diagnosed with CZS. CT scan slices: images a, c, i, j, and k. MRI images: b, d, e, f, g, h, k, and l. a (CT) and b (MRI): coarse and punctate calcifications at the cortico-subcortical junction, predominating in the frontal lobes. c: basal ganglia calcifications. d: marked microcephaly with redundant scalp skin in the occipital region. e: marked dilatation of supratentorial ventricular system, simplified gyral pattern of the brain, and prominence of the subarachnoid space in the frontal regions. f: malformations of cortical development compatible with polymicrogyria in the frontal lobes with sparing of posterior cortical areas. g: thin/hypoplastic corpus callosum. h: short corpus callosum with dysgenetic aspect. i and j: tetraventricular dilatation, simplified gyral pattern of the brain, cerebellar and pons hypoplasia, and cortico-subcortical and periventricular calcifications. k: asymmetric cerebellar hypoplasia with greater involvement of the right hemisphere, marked dilatation of the lateral ventricles with thinning of cerebral mantle, and prominence of cisterna magna. l: severe cerebellar hypoplasia