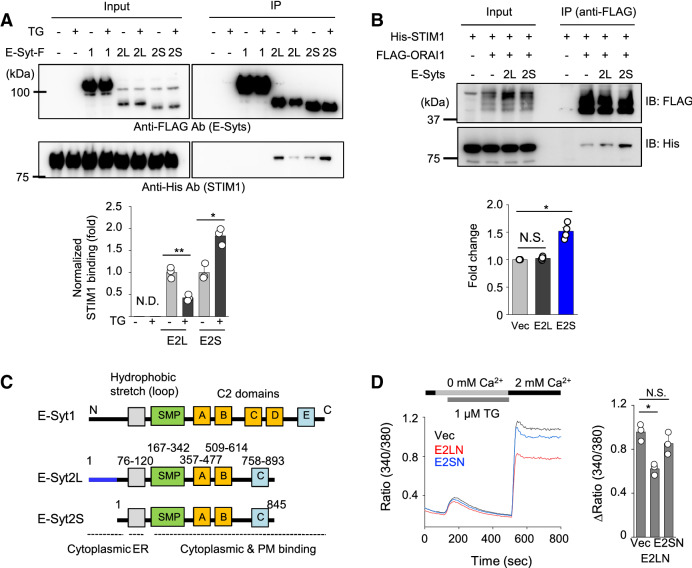
Figure 5.
Interaction between E-Syt2S and STIM1. (A) Interaction of E-Syts with STIM1. FLAG-immunoprecipitates from lysates of HEK293T cells expressing FLAG-tagged E-Syt1, E-Syt2L, or E-Syt2S together with His-tagged STIM1 were blotted for detection of the indicated proteins. Cells were treated with thapsigargin before lysis (1 μM TG for 10 min) in Ringer solution containing 2 mM Ca2+. Bar graph shows densitometry analysis of fold changes in STIM1 band intensity (normalized to individual immunoprecipitates) from three independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.005, N.D not detected. (B) Interaction of ORAI1 and STIM1 in the presence of E-Syt2L or E-Syt2S. FLAG-immunoprecipitates from lysates of HEK293T cells expressing FLAG-tagged ORAI1 together with His-tagged STIM1 were blotted for detection of the indicated proteins. Lysates of HEK293T cells expressing E-Syt2L or E-Syt2S were included in the binding reaction separately (see “Materials and methods" section). The bar graph shows densitometry analyses of fold changes in STIM1 band intensity (normalized to individual immunoprecipitates) from four independent experiments. *p < 0.05, N.S. not significant. (C) Schematic showing domain structure of E-Syt1, E-Syt2L and E-Syt2S. Grey boxes indicate transmembrane (TM) segments that span the ER membrane. Cytoplasmic region contains an N-terminal short fragment, a synaptotagmin-like mitochondrial lipid-binding protein (SMP) domain, and multiple C2 domains involved in targeting proteins to the plasma membrane. E-Syt2S lacks the first 48 amino acids present in E-Syt2L. (D) Measurement of SOCE in Jurkat T cells expressing N-terminus of E-Syt2L (E2LN) or E-Syt2S (E2SN). Intracellular stores were passively depleted with thapsigargin (1 μM, TG) in Ca2+-free solution, and SOCE was measured by perfusion with 2 mM Ca2+-containing solution. Traces show averaged SOCE responses from 30 to 50 cells, and bar graph shows averaged SOCE response ± S.E.M. from three independent experiments. *p < 0.05, N.S. not significant.