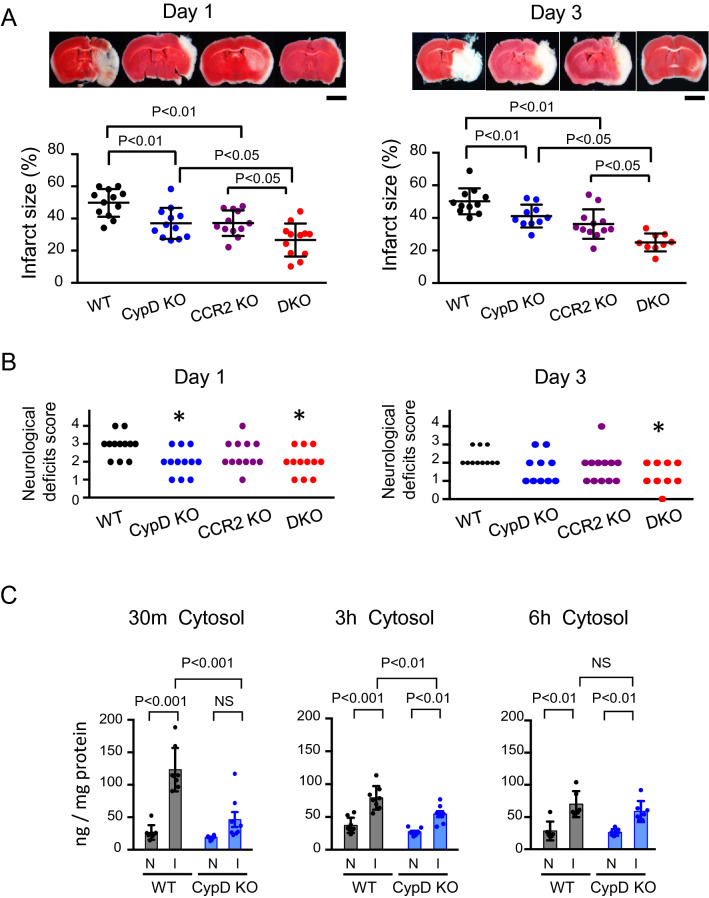
Figure 1.
Double knockout of CypD and CCR2 decreased cerebral IR injury compared to CypD- or CCR2-single knockout in mice. (A) Cross-sectional pictures of brains harvested 1 day and 3 days after IR injury. Graphs demonstrate quantitative results of TTC-negative infarct area. The data are represented as the mean ± SD (N = 9–12 mice per group), and they were analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison tests. Scale bar: 2 mm. (B) Neurological deficits score evaluated 1 day and 3 days after IR injury. Data were analyzed by the nonparametric Kruskal–Wallis test. *P < 0.05 versus WT mice. (C) Quantitative data of cytochrome c in the cytosol fraction isolated from brain tissues after IR injury. I: ischemic hemisphere, N: nonischemic hemisphere. The data represent the mean ± SD and compared using two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison tests.