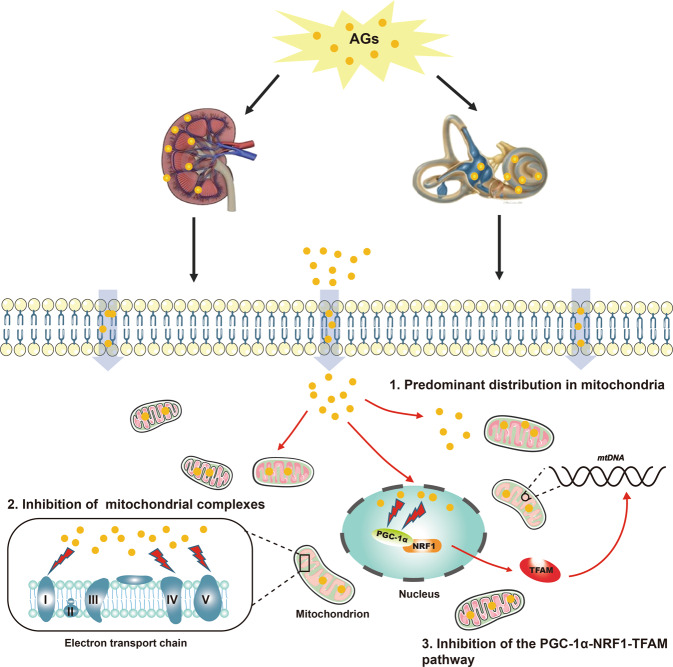
Fig. 9. Schematic representation of possible mechanisms of AG-induced nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity.
The schematic mainly includes three parts: (1) AGs are predominantly distributed in the mitochondria of renal tubular cells and inner ear hair cell-like cells; (2) AGs inhibit mitochondrial ETC complexes I, IV, and V; and (3) AGs inhibit the PGC-1α-NRF1-TFAM pathway, which may repress mitochondrial biosynthesis.